Table Population Mode
What Is a Table Population Mode?
The Table Population Mode determines how the target LU table is populated. There are four table population modes:
- Insert (default), the extracted record is inserted as a new record into the table.
- Upsert, the system checks via the Primary Key (PK) if the record already exists in the LU table. If the record does not exist, the new record is inserted into the table (similar to Insert mode). If the record already exists, the existing record is updated.
- Update, updates a record in a database table using the key column(s) marked in the target LU table. If a key column is not set in the target LU table, an Update is performed on all target records of each source record instead of updating a specific row.
- Delete, deletes a record in a database table using the key column(s) marked in the target LU table. If a key column is not set in the target LU table, a Delete is performed on all target records of each source record instead of deleting a specific row.
Update and Delete Modes - How Do I Set the Key on a Target LU Table?
If the population mode of the target LU table is set to Update or Delete, the key column(s) must be defined to enable the target LU table’s records to be updated or deleted correctly. The selected key column(s) is then added to the WHERE clause of the UPDATE or DELETE SQL statement.
To define a key:
- Check the checkbox on the left side of the Column Name. The color of the checkbox turns green.
- Mark one or several columns, if needed.
Example: Update the NEW_NOTE column of the target table ACTIVITY for each ACTIVITY_ID of the source object.
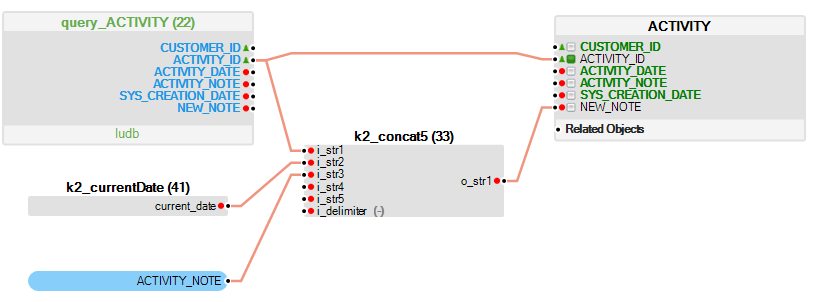
- The ACTIVITY_ID column on the target LU table is defined as a key column for the UPDATE statement.
- The k2_concat5 function maps the updated value to the NEW_NOTE column on ACTIVITY table.
- The value of the NEW_NOTE column in the target table ACTIVITY is updated based on the ACTIVITY_ID key of each entry in the source object.
Table Population Mode
What Is a Table Population Mode?
The Table Population Mode determines how the target LU table is populated. There are four table population modes:
- Insert (default), the extracted record is inserted as a new record into the table.
- Upsert, the system checks via the Primary Key (PK) if the record already exists in the LU table. If the record does not exist, the new record is inserted into the table (similar to Insert mode). If the record already exists, the existing record is updated.
- Update, updates a record in a database table using the key column(s) marked in the target LU table. If a key column is not set in the target LU table, an Update is performed on all target records of each source record instead of updating a specific row.
- Delete, deletes a record in a database table using the key column(s) marked in the target LU table. If a key column is not set in the target LU table, a Delete is performed on all target records of each source record instead of deleting a specific row.
Update and Delete Modes - How Do I Set the Key on a Target LU Table?
If the population mode of the target LU table is set to Update or Delete, the key column(s) must be defined to enable the target LU table’s records to be updated or deleted correctly. The selected key column(s) is then added to the WHERE clause of the UPDATE or DELETE SQL statement.
To define a key:
- Check the checkbox on the left side of the Column Name. The color of the checkbox turns green.
- Mark one or several columns, if needed.
Example: Update the NEW_NOTE column of the target table ACTIVITY for each ACTIVITY_ID of the source object.

- The ACTIVITY_ID column on the target LU table is defined as a key column for the UPDATE statement.
- The k2_concat5 function maps the updated value to the NEW_NOTE column on ACTIVITY table.
- The value of the NEW_NOTE column in the target table ACTIVITY is updated based on the ACTIVITY_ID key of each entry in the source object.




