HTTP Interface
The HTTP interface type defines the connections to an HTTP/s host and can be used by Broadway Actors.
To create a new HTTP interface, do the following:
Go to Project Tree > Shared Objects, right click Interfaces, select New Interface and then select HTTP from the Interface Type dropdown menu to open the New Interface window.
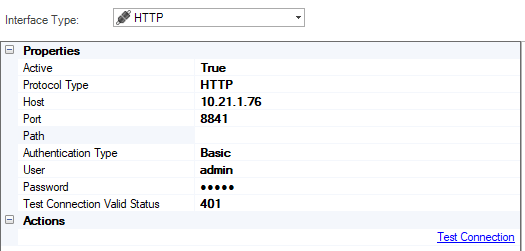
Populate the connection's settings and click Save.
Connection Settings
Authentication Settings
The Fabric HTTP Interface supports various standard authentication and authorization types (aka schemas) that can be used to access external protected resources.
Each Authentication Type (except for the None type) requires specific security credentials (provided by the resource provider) that are populated by the implementer into the HTTP Interface Properties and used by Fabric to authenticate remote vendor servers.
Fabric supports the following:
Basic HTTP Authentication - built into the HTTP protocol. Fabric (the client) sends HTTP requests with the
Authorizationheader that contains the wordBasicfollowed by <user:password> in base64-encoded form. This interface requires the following properties:- User
- Password
Note: this mechanism does not provide confidentiality, hence it is usually used over HTTPS and not HTTP.
Bearer Authentication (aka token authentication) - an HTTP Authentication Type/schema that uses cryptic string security tokens called Bearer Tokens. Fabric (the client) sends this token in the
Authorizationheader when sending requests to a resource. This interface requires the following properties:- token
OAuth 2.0 Password Credentials - an OAuth protocol's grant type flow. Fabric (the client) first interacts with an authorization server, provides a user and password and gets an access token which is then used for the resource server's calls. This interface requires the following properties:
User
Password
Access Token URL - address of the authorization server providing the access token.
Client ID - provided by the external resource/authorized vendor.
Client Secret - provided by the external resource/authorized vendor. Note that although the Client Server is encrypted and saved it is displayed in clear text in the Fabric Studio.
Scope (optional) - validates that the required actions are permitted by the authenticating server which returns the access token's scope to the client. The value of the scope parameter is expressed as a list of space-delimited, case-sensitive strings.
Token Timeout - requests timeout to the authorization server.
OAuth 2.0 Password Credentials - Basic Auth Headers - an OAuth protocol grant type flow. It is similar to "OAuth 2.0 Password Credentials" but in this type Fabric provides the User and Password to the authorization server in the request header, rather than in the request body. This type is more recommended and is considered as best practice.
OAuth 2.0 Client Credentials - an OAuth protocol grant type flow. Fabric provides the client-ID and Client-Secret to the authorization server which returns the access token used by Fabric for the resource's server calls. This interface requires the following properties in Fabric:
Client ID - provided by the external resource/authorized vendor.
Client Secret - provided by the external resource/authorized vendor. Note that although the secret key is encrypted and saved, it is displayed in clear text in the Fabric Studio.
Scope (optional) - specifies the scope of the access request. In turn, the authorization server uses the scope response parameter to inform the client of the scope of the access token issued. The value of the scope is expressed as a list of space-delimited, case-sensitive strings.
Token Timeout - requests timeout to the authorization server.
OAuth 2.0 Client Credentials - Basic Auth Headers - an OAuth protocol grant type flow. It is similar to "OAuth 2.0 Client Credentials" but in this type Fabric provides the client-ID and Client-Secret to the authorization server in the request header, rather than in the request body. This type is more recommended.
If the service provider does not require authentication, select None in the Authentication Type.
Example of Calling a WS via HTTP Interface in a Broadway Flow
The above Broadway flow uses an Http Actor to connect to the HTTP server that populates the predefined HTTP interface into the interface input argument. The path input argument must be populated by the relative path to the interface. The params input argument must be populated when relevant. The format input argument must be populated with the required output format, e.g. JSON.
For example, in order to invoke a Fabric Web Service, do the following:
Define HTTP interface with the relevant authentication type, e.g. Bearer, and set the Token value.
In a Broadway flow, use either Http or HttpJson Actor to invoke a WS. Populate the input arguments as follows:
Set interface to the predefined Http interface.
Set path to the WS, relative to the interface. For example:
/api/isAlive- When the interface receives input parameters, they can be sent using the params input argument. Then the path will look like this:
/api/wsCustomerSSN?- When using Http Actor, set format input argument to be the required output format, e.g. JSON.
Use a JsonParser Actor to parse the WS output.
HTTP Interface
The HTTP interface type defines the connections to an HTTP/s host and can be used by Broadway Actors.
To create a new HTTP interface, do the following:
Go to Project Tree > Shared Objects, right click Interfaces, select New Interface and then select HTTP from the Interface Type dropdown menu to open the New Interface window.

Populate the connection's settings and click Save.
Connection Settings
Authentication Settings
The Fabric HTTP Interface supports various standard authentication and authorization types (aka schemas) that can be used to access external protected resources.
Each Authentication Type (except for the None type) requires specific security credentials (provided by the resource provider) that are populated by the implementer into the HTTP Interface Properties and used by Fabric to authenticate remote vendor servers.
Fabric supports the following:
Basic HTTP Authentication - built into the HTTP protocol. Fabric (the client) sends HTTP requests with the
Authorizationheader that contains the wordBasicfollowed by <user:password> in base64-encoded form. This interface requires the following properties:- User
- Password
Note: this mechanism does not provide confidentiality, hence it is usually used over HTTPS and not HTTP.
Bearer Authentication (aka token authentication) - an HTTP Authentication Type/schema that uses cryptic string security tokens called Bearer Tokens. Fabric (the client) sends this token in the
Authorizationheader when sending requests to a resource. This interface requires the following properties:- token
OAuth 2.0 Password Credentials - an OAuth protocol's grant type flow. Fabric (the client) first interacts with an authorization server, provides a user and password and gets an access token which is then used for the resource server's calls. This interface requires the following properties:
User
Password
Access Token URL - address of the authorization server providing the access token.
Client ID - provided by the external resource/authorized vendor.
Client Secret - provided by the external resource/authorized vendor. Note that although the Client Server is encrypted and saved it is displayed in clear text in the Fabric Studio.
Scope (optional) - validates that the required actions are permitted by the authenticating server which returns the access token's scope to the client. The value of the scope parameter is expressed as a list of space-delimited, case-sensitive strings.
Token Timeout - requests timeout to the authorization server.
OAuth 2.0 Password Credentials - Basic Auth Headers - an OAuth protocol grant type flow. It is similar to "OAuth 2.0 Password Credentials" but in this type Fabric provides the User and Password to the authorization server in the request header, rather than in the request body. This type is more recommended and is considered as best practice.
OAuth 2.0 Client Credentials - an OAuth protocol grant type flow. Fabric provides the client-ID and Client-Secret to the authorization server which returns the access token used by Fabric for the resource's server calls. This interface requires the following properties in Fabric:
Client ID - provided by the external resource/authorized vendor.
Client Secret - provided by the external resource/authorized vendor. Note that although the secret key is encrypted and saved, it is displayed in clear text in the Fabric Studio.
Scope (optional) - specifies the scope of the access request. In turn, the authorization server uses the scope response parameter to inform the client of the scope of the access token issued. The value of the scope is expressed as a list of space-delimited, case-sensitive strings.
Token Timeout - requests timeout to the authorization server.
OAuth 2.0 Client Credentials - Basic Auth Headers - an OAuth protocol grant type flow. It is similar to "OAuth 2.0 Client Credentials" but in this type Fabric provides the client-ID and Client-Secret to the authorization server in the request header, rather than in the request body. This type is more recommended.
If the service provider does not require authentication, select None in the Authentication Type.
Example of Calling a WS via HTTP Interface in a Broadway Flow
The above Broadway flow uses an Http Actor to connect to the HTTP server that populates the predefined HTTP interface into the interface input argument. The path input argument must be populated by the relative path to the interface. The params input argument must be populated when relevant. The format input argument must be populated with the required output format, e.g. JSON.
For example, in order to invoke a Fabric Web Service, do the following:
Define HTTP interface with the relevant authentication type, e.g. Bearer, and set the Token value.
In a Broadway flow, use either Http or HttpJson Actor to invoke a WS. Populate the input arguments as follows:
Set interface to the predefined Http interface.
Set path to the WS, relative to the interface. For example:
/api/isAlive- When the interface receives input parameters, they can be sent using the params input argument. Then the path will look like this:
/api/wsCustomerSSN?- When using Http Actor, set format input argument to be the required output format, e.g. JSON.
Use a JsonParser Actor to parse the WS output.




