iidFinder
Try to reduce the number of levels in the staging.xml\iidFinder.xml . If applicable (e.g. the table contains the LUID field), set the table as a first level.
The latest iidFinder implementation is tested with sourceAvailable set to false, make sure you use this setting.
- If this property is not set in your project, the default is true. If you are using the previous implementation version, special scenarios will not be supported (LCK, LPK & Cross instances).
Setting store=false in the iidFinder\staging.xml :
Even if the table does not have subordinate tables, it is recommended to save the cache data for it.
Store can be set to false only in the case when this table has no subordinate tables and when the link field will always be presented in the Kafka message (Either it is a PK field or the GG extract is defined as all_column_ind = true).
Rules to delete data from the LU (for example, purging of old records):
Apply a change to execute the purging only when an update is received for the specific table and not for every sync (Using the generic trnExecUserActivity).
Records must be deleted from the cache tables as well, otherwise, iidFinder will continue linking insert\update of the subordinate tables for deleted records. Use the addDeleteFinder plus runDeleteFinder APIs to delete these records from the cache.
Execute Enrichment functionality only when required.
Make sure the enrichment is executed only once a message was received for the relevant table.
Use trnExecUserActivity functionality to set the relevant thread global.
Do not extract from a source in case of a new instance.
Use EXTRACT_FROM_SOURCE_IND = false and add the iidFinder generic LU decision function: fnIIDFCheckExtractFromSourceInd .
Make sure that there are no scenarios that cannot be supported. For example, records which were orphans on the source before the new instance was created.
IIDF Root setting:
The following is the correct setting:
Truncate = false
Unique index on the IID
population mode = upsert
If the truncate mode is set to “true”, the deleteOrphans functionality for an LPK scenario on a table that is connected to the root might trigger the deletion of records which should not be deleted.
IIDF_SOURCE_DELAY is used to rearrange transactions from different DCs or to re-execute a transaction after extract from a source that might receive a delayed update transaction. If the EXTRACT_FROM_SOURCE is set to “false” and there is no multi-DC cluster, there is no point in saving the transactions in the queue. It will just consume additional space.
Lookup tables in Cassandra: Apply Kafka transactions.
Update the lookup table in Cassandra using a job consumer and not an enrichment function. If enrichment is used, such as when the delta record was not synced yet, the lookup will not be updated and the web service will return no data found. Generic lookup consumer information can be found in the COE knowledge base.
As the lookup is usually built from only a few fields of the original table, create a separate topic for it (if possible). Apply filtering that will cause a message to be published to this topic if even only one of the columns gets changed. This can be done on the GG replicat to Kafka and will reduce the load from the consumer and the cluster.
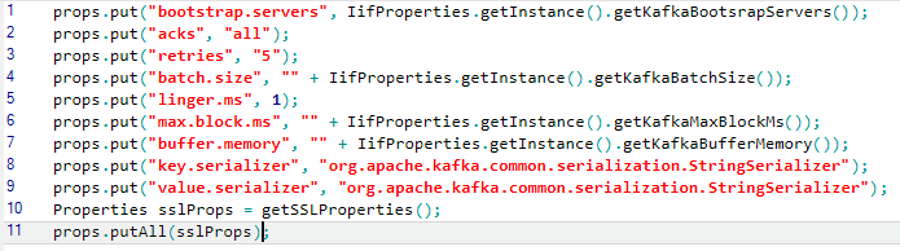
Do not store the iidFinder Kafka details in a translation table. Use IifProperties.getInstance() to get the iidFinder configuration setting of the cluster. See this example:
NOTE: Kafka Producer & Consumer examples can be found in the COE knowledge base project.
Kafka Delta get jobs – If you are using the Kafka delta topic for the get mechanism, it is very important to set all globals and iifConfig parameters correctly. Otherwise, data might not be deleted from Delta or ‘sync’ might be skipped.
DELTA_JOB_DELAY_TIME should be set to a higher value than the DELTA_RANGE_DELAY_MS to ensure that the records will be deleted. The delete formula is as follows: MAX_DC_UPDATE – DELTA_EXTRA_TIME_MS < Delta records update_time < CURRENT_TIME - DELTA_RANGE_DELAY_MS
Note that in this formula CURRENT_TIME means get time.
DELTA_JOB_PREV_MESSAGE_DIFF_EPSILON_MS – The parser skips a transaction if the IID previous sync time is higher than the the transaction handle time. The EPSILON parameter is used in order to avoid skipping a transaction which was not handled yet due to Cassandra nodes time differences. Meaning if we set it to 2 seconds and instance 111 was synced on 10:00:05, a get for a transaction which was handled by iidFinder on 10:00:02 for the same instance will be skipped. However, a transaction which was handled by iidFinder on 10:00:04 for the same instance will not be skipped.
Make sure you are using the latest version of the iidFinder library (available from the GIT repository).
iidFinder
Try to reduce the number of levels in the staging.xml\iidFinder.xml . If applicable (e.g. the table contains the LUID field), set the table as a first level.
The latest iidFinder implementation is tested with sourceAvailable set to false, make sure you use this setting.
- If this property is not set in your project, the default is true. If you are using the previous implementation version, special scenarios will not be supported (LCK, LPK & Cross instances).
Setting store=false in the iidFinder\staging.xml :
Even if the table does not have subordinate tables, it is recommended to save the cache data for it.
Store can be set to false only in the case when this table has no subordinate tables and when the link field will always be presented in the Kafka message (Either it is a PK field or the GG extract is defined as all_column_ind = true).
Rules to delete data from the LU (for example, purging of old records):
Apply a change to execute the purging only when an update is received for the specific table and not for every sync (Using the generic trnExecUserActivity).
Records must be deleted from the cache tables as well, otherwise, iidFinder will continue linking insert\update of the subordinate tables for deleted records. Use the addDeleteFinder plus runDeleteFinder APIs to delete these records from the cache.
Execute Enrichment functionality only when required.
Make sure the enrichment is executed only once a message was received for the relevant table.
Use trnExecUserActivity functionality to set the relevant thread global.
Do not extract from a source in case of a new instance.
Use EXTRACT_FROM_SOURCE_IND = false and add the iidFinder generic LU decision function: fnIIDFCheckExtractFromSourceInd .
Make sure that there are no scenarios that cannot be supported. For example, records which were orphans on the source before the new instance was created.
IIDF Root setting:
The following is the correct setting:
Truncate = false
Unique index on the IID
population mode = upsert
If the truncate mode is set to “true”, the deleteOrphans functionality for an LPK scenario on a table that is connected to the root might trigger the deletion of records which should not be deleted.
IIDF_SOURCE_DELAY is used to rearrange transactions from different DCs or to re-execute a transaction after extract from a source that might receive a delayed update transaction. If the EXTRACT_FROM_SOURCE is set to “false” and there is no multi-DC cluster, there is no point in saving the transactions in the queue. It will just consume additional space.
Lookup tables in Cassandra: Apply Kafka transactions.
Update the lookup table in Cassandra using a job consumer and not an enrichment function. If enrichment is used, such as when the delta record was not synced yet, the lookup will not be updated and the web service will return no data found. Generic lookup consumer information can be found in the COE knowledge base.
As the lookup is usually built from only a few fields of the original table, create a separate topic for it (if possible). Apply filtering that will cause a message to be published to this topic if even only one of the columns gets changed. This can be done on the GG replicat to Kafka and will reduce the load from the consumer and the cluster.
Do not store the iidFinder Kafka details in a translation table. Use IifProperties.getInstance() to get the iidFinder configuration setting of the cluster. See this example:
NOTE: Kafka Producer & Consumer examples can be found in the COE knowledge base project.

Kafka Delta get jobs – If you are using the Kafka delta topic for the get mechanism, it is very important to set all globals and iifConfig parameters correctly. Otherwise, data might not be deleted from Delta or ‘sync’ might be skipped.
DELTA_JOB_DELAY_TIME should be set to a higher value than the DELTA_RANGE_DELAY_MS to ensure that the records will be deleted. The delete formula is as follows: MAX_DC_UPDATE – DELTA_EXTRA_TIME_MS < Delta records update_time < CURRENT_TIME - DELTA_RANGE_DELAY_MS
Note that in this formula CURRENT_TIME means get time.
DELTA_JOB_PREV_MESSAGE_DIFF_EPSILON_MS – The parser skips a transaction if the IID previous sync time is higher than the the transaction handle time. The EPSILON parameter is used in order to avoid skipping a transaction which was not handled yet due to Cassandra nodes time differences. Meaning if we set it to 2 seconds and instance 111 was synced on 10:00:05, a get for a transaction which was handled by iidFinder on 10:00:02 for the same instance will be skipped. However, a transaction which was handled by iidFinder on 10:00:04 for the same instance will not be skipped.
Make sure you are using the latest version of the iidFinder library (available from the GIT repository).




