Invoking an HTTP REST Call
This example demonstrates how a Telco mobile carrier responds to customers complaining about bad service using a REST API to reveal the location (country, city, long and lat coordinates) of a customer via their current IP domain.
Let's assume that a feed updates Fabric with data about the carrier's regional problems and that this information is stored in a Fabric reference table. When customers contact the Call Center to complain, a match is made between their current location and the reference table. To do so, the carrier's CRM calls the Fabric Web Service whose response indicates whether the customer is located in a known bad service area.
Example
The following example features a REST API call to the IP-API geolocation service which responds in JSON format parsed via a JSON parser provided in an external JAR. Note that in this scenario external JAR handling guidelines have been omitted.
This example also uses a Web Service. For more information about creating Web Services in Fabric, click here.
Preparation
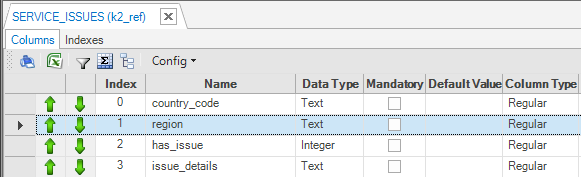
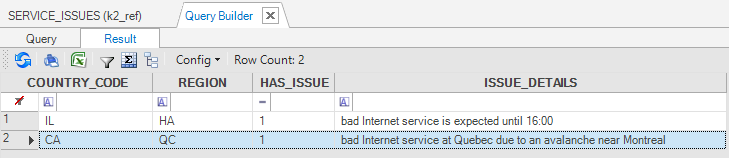
Create a new SERVICE_ISSUES reference table and populate it with 2 rows to simulate the feed process.
Implementation
Download the org.json JAR file from org.json and save it in the Fabric JARs directory. For more information about this library, click here.
Add the following import statements to the Logic file and save it in Web Service > Translation directory/category ("k2_ws\Translation"):
import org.json.JSONObject;
import org.json.JSONArray;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
The first 2 lines parse the JSON. The other rows perform the HTTP call via Java internal support and therefore an external JAR is not required.
The following example displays Web Service code which gets the userIP input parameter and returns a string with the status and information.
log.info("wsTrnIpToLocationREST");
String issueStatusDetails = "No issues were found at customer's region";
String SQLREF="SELECT ISSUE_DETAILS from SERVICE_ISSUES where COUNTRY_CODE = ? and REGION = ? and HAS_ISSUE = 1";
URL url = new URL("http://ip-api.com/json/" + userIP);
HttpURLConnection con = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
con.setRequestMethod("GET");
int responseCode = con.getResponseCode();
log.info("wsTrnIpToLocationREST - Response code for user domain IP " + userIP + ": " + responseCode);
if (responseCode == 200) {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(con.getInputStream()));
String inputLine;
StringBuffer content = new StringBuffer();
while ((inputLine = in.readLine()) != null) {
content.append(inputLine);
}
in.close();
JSONObject jsonResponse = new JSONObject(content.toString());
String countryCode = jsonResponse.getString("countryCode");
log.info("countryCode: " + countryCode);
String region = jsonResponse.getString("region");
log.info("region: " + region);
//log.info("city: " + jsonResponse.getString("city"));
//log.info("lon: " + jsonResponse.getNumber("lon"));
//log.info("lat: " + jsonResponse.getNumber("lat"));
String issueStatusDB = fabric().fetch(SQLREF,countryCode,region).firstValue().toString();
log.info("status: " + issueStatusDB);
if ((issueStatusDB != null) && (!issueStatusDB.isEmpty())) {
issueStatusDetails = issueStatusDB;
}
} else {
log.info("The request call was failed");
}
con.disconnect();
return issueStatusDetails;
Web Service steps:
Search for the userIP input parameter and call the REST API service to get information:
- If a good response is returned, parse it and take the countryCode and the region.
- Check for an open entry in SERVICE_ISSUES (has_issue = 1) for this country-code and region.
- If an open issue is found, set it as the Web Service result string.
The following displays how the the Web Service gets input IP = "24.48.0.1":
### Authentication & Authorization
A REST API may require that authentication and authorization is sent as headers. In the java.net library used in this example, this can be implemented using the setRequestProperty method. For example, if the API provider supplies a username and passwords and works with basic authentication, the following can be used:
String encoded = Base64.encode(username+":"+password);
cons.setRequestProperty("Authorization", "Basic "+encoded);
Note that there are alternative HTTPP client JAR, such as apache, which already have the specific setHeader method.
Invoking an HTTP REST Call
This example demonstrates how a Telco mobile carrier responds to customers complaining about bad service using a REST API to reveal the location (country, city, long and lat coordinates) of a customer via their current IP domain.
Let's assume that a feed updates Fabric with data about the carrier's regional problems and that this information is stored in a Fabric reference table. When customers contact the Call Center to complain, a match is made between their current location and the reference table. To do so, the carrier's CRM calls the Fabric Web Service whose response indicates whether the customer is located in a known bad service area.
Example
The following example features a REST API call to the IP-API geolocation service which responds in JSON format parsed via a JSON parser provided in an external JAR. Note that in this scenario external JAR handling guidelines have been omitted.
This example also uses a Web Service. For more information about creating Web Services in Fabric, click here.
Preparation
Create a new SERVICE_ISSUES reference table and populate it with 2 rows to simulate the feed process.


Implementation
Download the org.json JAR file from org.json and save it in the Fabric JARs directory. For more information about this library, click here.
Add the following import statements to the Logic file and save it in Web Service > Translation directory/category ("k2_ws\Translation"):
import org.json.JSONObject;
import org.json.JSONArray;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
The first 2 lines parse the JSON. The other rows perform the HTTP call via Java internal support and therefore an external JAR is not required.
The following example displays Web Service code which gets the userIP input parameter and returns a string with the status and information.
log.info("wsTrnIpToLocationREST");
String issueStatusDetails = "No issues were found at customer's region";
String SQLREF="SELECT ISSUE_DETAILS from SERVICE_ISSUES where COUNTRY_CODE = ? and REGION = ? and HAS_ISSUE = 1";
URL url = new URL("http://ip-api.com/json/" + userIP);
HttpURLConnection con = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
con.setRequestMethod("GET");
int responseCode = con.getResponseCode();
log.info("wsTrnIpToLocationREST - Response code for user domain IP " + userIP + ": " + responseCode);
if (responseCode == 200) {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(con.getInputStream()));
String inputLine;
StringBuffer content = new StringBuffer();
while ((inputLine = in.readLine()) != null) {
content.append(inputLine);
}
in.close();
JSONObject jsonResponse = new JSONObject(content.toString());
String countryCode = jsonResponse.getString("countryCode");
log.info("countryCode: " + countryCode);
String region = jsonResponse.getString("region");
log.info("region: " + region);
//log.info("city: " + jsonResponse.getString("city"));
//log.info("lon: " + jsonResponse.getNumber("lon"));
//log.info("lat: " + jsonResponse.getNumber("lat"));
String issueStatusDB = fabric().fetch(SQLREF,countryCode,region).firstValue().toString();
log.info("status: " + issueStatusDB);
if ((issueStatusDB != null) && (!issueStatusDB.isEmpty())) {
issueStatusDetails = issueStatusDB;
}
} else {
log.info("The request call was failed");
}
con.disconnect();
return issueStatusDetails;
Web Service steps:
Search for the userIP input parameter and call the REST API service to get information:
- If a good response is returned, parse it and take the countryCode and the region.
- Check for an open entry in SERVICE_ISSUES (has_issue = 1) for this country-code and region.
- If an open issue is found, set it as the Web Service result string.
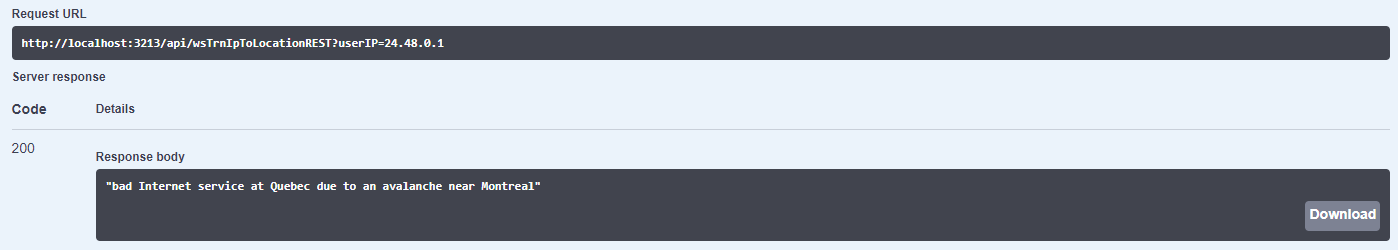
The following displays how the the Web Service gets input IP = "24.48.0.1":

### Authentication & Authorization
A REST API may require that authentication and authorization is sent as headers. In the java.net library used in this example, this can be implemented using the setRequestProperty method. For example, if the API provider supplies a username and passwords and works with basic authentication, the following can be used:
String encoded = Base64.encode(username+":"+password);
cons.setRequestProperty("Authorization", "Basic "+encoded);
Note that there are alternative HTTPP client JAR, such as apache, which already have the specific setHeader method.




