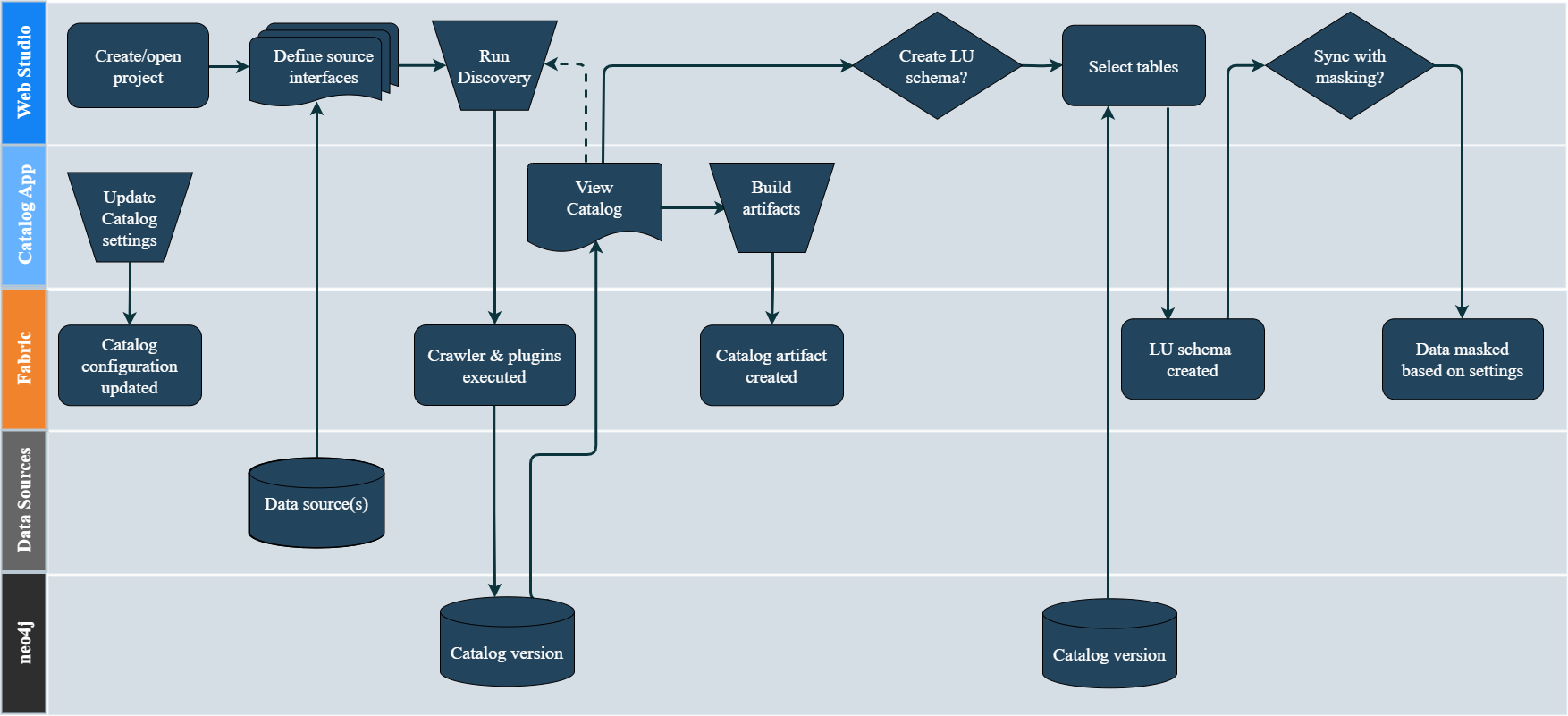
Discovery Process
The K2view Discovery process is depicted in the below diagram and it includes the following major steps:
Define a Fabric interface for a given data source and initiate the Discovery job.
The first step of the Discovery job is a Crawler. It scans the data source while identifying the existing entities and the relationships between them. The Crawler's output is the Catalog schema.
Next, a Plugin Framework is triggered automatically upon completion of the Crawler's process. The Plugin Framework is a platform for executing predefined rules (plugins) to run on the Catalog schema and to enhance it accordingly. Examples of plugins are:
- Creating a referential link between 2 objects, based on field names matching rules.
- Classification of fields based on field data and/or field name - as email, phone, social security number, etc.
- Determining whether a field should be marked as PII.
Upon completion of the Plugin Framework execution, the Catalog schema is saved into the neo4j Graph DB and it can be viewed via the Catalog application.
The Catalog supports the following actions:
- Versioning - a new version is created when the Discovery job identifies changes in a data source or in the Catalog plugin rules while comparing with the previous Catalog version. By default, the Catalog application displays the latest version.
- Manual overrides - editing of the Catalog's latest version is available in the Catalog application, and it includes updating of the Catalog nodes' properties and editing of the relations between the nodes.
- The Catalog artifact (including the identified classifications and PII indications) can be built and saved into the Project tree, in order to be used by the Catalog Masking mechanism.
Once the process has been completed, the Logical Unit schema can be created based on the Catalog's version. In addition, the data can be masked during the sync process by using the Catalog Masking actors.
Discovery Process
The K2view Discovery process is depicted in the below diagram and it includes the following major steps:
Define a Fabric interface for a given data source and initiate the Discovery job.
The first step of the Discovery job is a Crawler. It scans the data source while identifying the existing entities and the relationships between them. The Crawler's output is the Catalog schema.
Next, a Plugin Framework is triggered automatically upon completion of the Crawler's process. The Plugin Framework is a platform for executing predefined rules (plugins) to run on the Catalog schema and to enhance it accordingly. Examples of plugins are:
- Creating a referential link between 2 objects, based on field names matching rules.
- Classification of fields based on field data and/or field name - as email, phone, social security number, etc.
- Determining whether a field should be marked as PII.
Upon completion of the Plugin Framework execution, the Catalog schema is saved into the neo4j Graph DB and it can be viewed via the Catalog application.
The Catalog supports the following actions:
- Versioning - a new version is created when the Discovery job identifies changes in a data source or in the Catalog plugin rules while comparing with the previous Catalog version. By default, the Catalog application displays the latest version.
- Manual overrides - editing of the Catalog's latest version is available in the Catalog application, and it includes updating of the Catalog nodes' properties and editing of the relations between the nodes.
- The Catalog artifact (including the identified classifications and PII indications) can be built and saved into the Project tree, in order to be used by the Catalog Masking mechanism.
Once the process has been completed, the Logical Unit schema can be created based on the Catalog's version. In addition, the data can be masked during the sync process by using the Catalog Masking actors.





