Task Execution Processes
This article describes the task execution's steps and the TDM processes of each step.
The Task Execution process consists of the following steps:
- Creating a task execution request.
- Initiating Batch processes for the task's pre-execution processes.
- Initiating Batch processes for the task's entities and/or tables.
- Initiating Batch processes for the task's post-execution processes
- Updating the status of the completed processes.
All Batch processes run in an asynchronous mode.
A Task Execution process can be initiated either from the TDM Portal, a direct call to the start task execution API, or via a TDM Scheduling process.
A task can include entities and/or tables. All tasks that run on a Business Entity can have pre-execution and/or post-execution processes based on the BE's definition. For example, sending an email to a user after a task has been executed.
The following diagram displays the task execution process for entities:
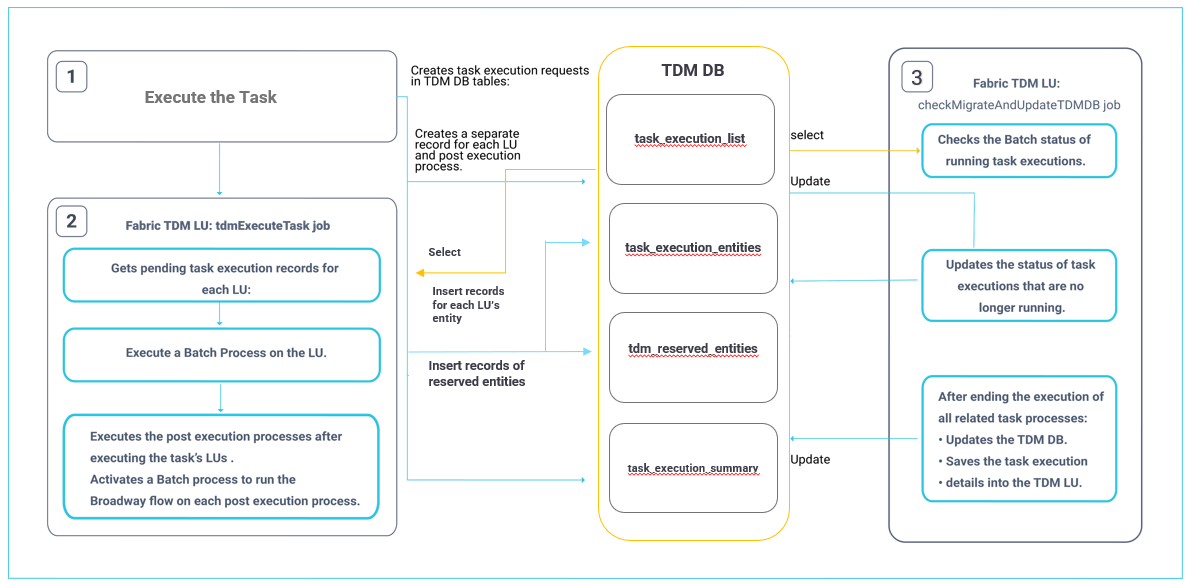
Main TDM Task Execution Process: tdmExecuteTask Job
This job runs every 10 seconds and scans the task_execution_list in the TDM DB table to get pending task execution requests.
Each task execution gets a unique task_execution_id identifier. A task execution may include several LUs and post-execution processes, each with a separate record in the task_execution_list. All records related to a given task execution have the same task_execution_id.
The execution order of the related task's components is as follows:
Running of the LUs (from parent to child). Processing of all related entities on each LU before moving to the child LU's execution. Click for more information about the execution order of the hierarchical LUs.
Running of the post-execution processes after the execution of the LUs ends. Post-execution processes are executed according to their execution order as defined in the task's BE.
The following diagram describes the main TDM task execution process on Business Entities and referential tables:
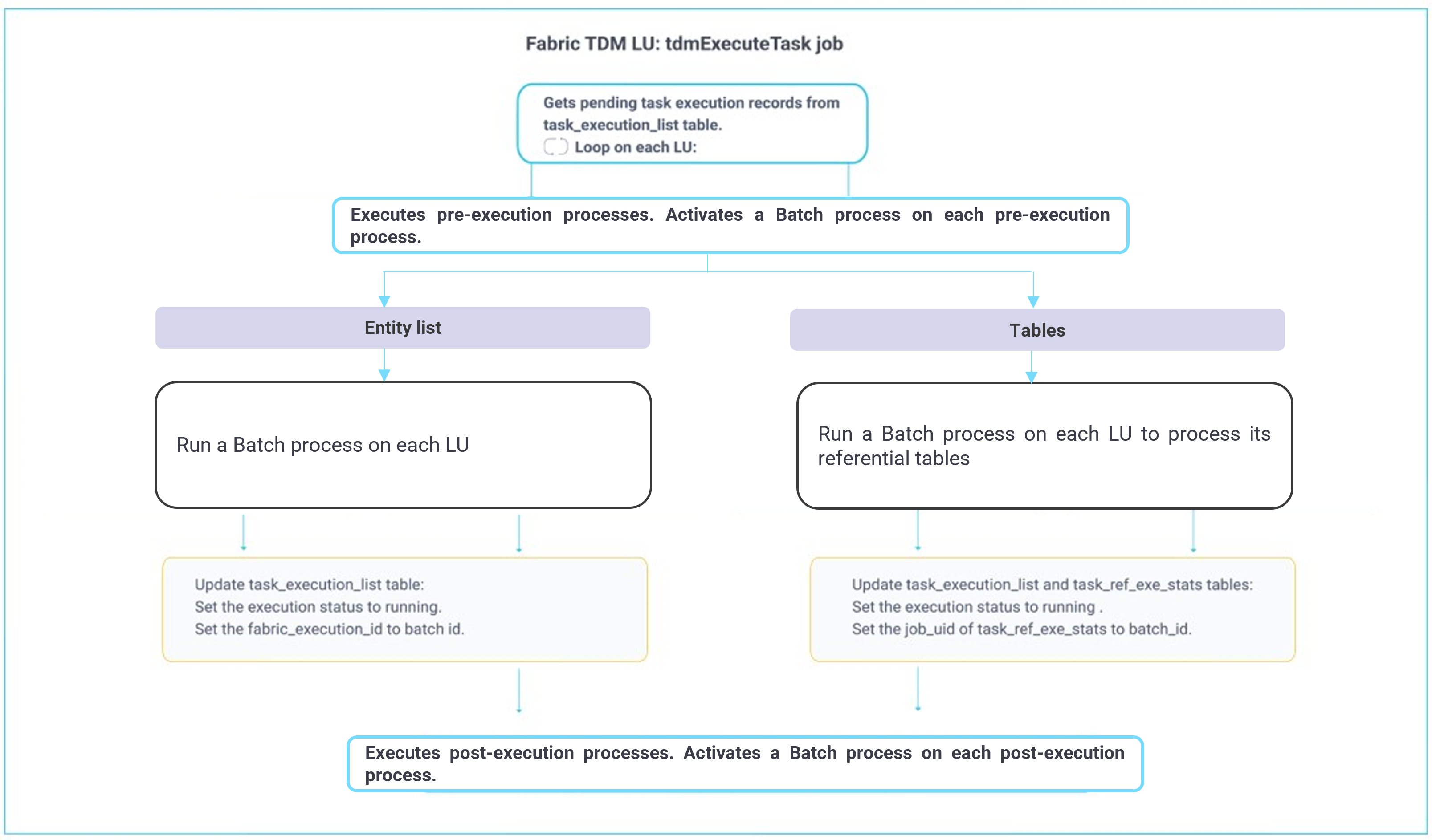
The execution is implemented in an asynchronous mode. The tdmExecuteTask job starts the execution on each Batch process in an asynchronous mode, and a separate TDM job - checkMigrateAndUpdateTDMDB - checks and updates the execution status of each process.
Both jobs must be executed in parallel.
Example:
- The execution of a task with Customer and Billing LUs and with a post-execution process that sends an email when the task execution ends. The Customer is the parent LU of Billing.
- 3 records are created in the task_execution_list on this task; all have the same task_execution_id.
- The tdmExecuteTask job executes the Batch process on the Customer LU.
- The checkMigrateAndUpdateTDMDB job updates the status of Customer LU after the execution has been completed.
- The tdmExecuteTask job starts executing Billing LU after the Customer LU (Billing's parent LU) is marked as completed.
- The checkMigrateAndUpdateTDMDB job updates the status of Billing LU after the execution has been completed.
- The tdmExecuteTask job can start executing the post-execution process after completing the execution of all the task's LUs.
The following diagram describes the main TDM task execution process on a task with tables only:

Click here for more information about task's tables handling.
checkMigrateAndUpdateTDMDB Job
This job runs every 10 seconds and checks the execution status of the running process. It selects records from the task_execution_list in the TDM DB table where the execution_status is running.
The execution status is being checked as follows:
- If the task contains selected tables to be processed - it checks the execution status of all related tables in task_exe_ref_stats in the TDM DB table.
- It checks the batch status based on the batch_id populated in task_execution_list.fabric_execution_id column by the tdmExecuteTask job.
When the process has been completed, the following TDM DB tables are updated by this job:
- task_execution_list, updates the execution_status and additional data.
- task_execution_entities, populates each entity or table and its status. Sets the id_type to ENTITY or REFERENCE according to the entity or to the table data type.
- task_exe_error_detailed, populates the execution errors in Extract tasks. Note that the execution errors of Load tasks are reported to this table by the PopulateTableErrors Actor.
A new Global has been added in TDM 8.1: TDM_BATCH_LIMIT. This Global enables limiting the number of entities to be populated into the TDM execution tables per task execution. From Fabric 7.2 onwards, it is possible to populate the LIMIT parameter of the batch_details command with -1 to get all batch's entities without a limit. Therefore, the TDM_BATCH_LIMIT Global is set to -1 by default, allowing to get all the batch's entities and populate them into the TDM DB during the task execution.
Handling Task Executions that have been Completed
A task execution is considered complete when it no longer has pending or running executions. The checkMigrateAndUpdateTDMDB job handles task executions that have been completed - as follows:
- It updates the execution summary in the TDM DB tables.
- It synchronizes the task execution details to Fabric: Each task execution is stored as an LUI in the TDM LU.
Updating the Task Executions Summary Table
Updates the following TDM DB table:
Syncing the Task Execution ID to TDM LU
The TDM LU holds the execution details of each task execution. The TDM's instance ID is the task_execution_id generated for each task execution.
A completed task execution is synchronized into the TDM LU. The execution information and the TDM execution reports are extracted from the TDM LUI data.
Task Execution Processes
This article describes the task execution's steps and the TDM processes of each step.
The Task Execution process consists of the following steps:
- Creating a task execution request.
- Initiating Batch processes for the task's pre-execution processes.
- Initiating Batch processes for the task's entities and/or tables.
- Initiating Batch processes for the task's post-execution processes
- Updating the status of the completed processes.
All Batch processes run in an asynchronous mode.
A Task Execution process can be initiated either from the TDM Portal, a direct call to the start task execution API, or via a TDM Scheduling process.
A task can include entities and/or tables. All tasks that run on a Business Entity can have pre-execution and/or post-execution processes based on the BE's definition. For example, sending an email to a user after a task has been executed.
The following diagram displays the task execution process for entities:

Main TDM Task Execution Process: tdmExecuteTask Job
This job runs every 10 seconds and scans the task_execution_list in the TDM DB table to get pending task execution requests.
Each task execution gets a unique task_execution_id identifier. A task execution may include several LUs and post-execution processes, each with a separate record in the task_execution_list. All records related to a given task execution have the same task_execution_id.
The execution order of the related task's components is as follows:
Running of the LUs (from parent to child). Processing of all related entities on each LU before moving to the child LU's execution. Click for more information about the execution order of the hierarchical LUs.
Running of the post-execution processes after the execution of the LUs ends. Post-execution processes are executed according to their execution order as defined in the task's BE.
The following diagram describes the main TDM task execution process on Business Entities and referential tables:

The execution is implemented in an asynchronous mode. The tdmExecuteTask job starts the execution on each Batch process in an asynchronous mode, and a separate TDM job - checkMigrateAndUpdateTDMDB - checks and updates the execution status of each process.
Both jobs must be executed in parallel.
Example:
- The execution of a task with Customer and Billing LUs and with a post-execution process that sends an email when the task execution ends. The Customer is the parent LU of Billing.
- 3 records are created in the task_execution_list on this task; all have the same task_execution_id.
- The tdmExecuteTask job executes the Batch process on the Customer LU.
- The checkMigrateAndUpdateTDMDB job updates the status of Customer LU after the execution has been completed.
- The tdmExecuteTask job starts executing Billing LU after the Customer LU (Billing's parent LU) is marked as completed.
- The checkMigrateAndUpdateTDMDB job updates the status of Billing LU after the execution has been completed.
- The tdmExecuteTask job can start executing the post-execution process after completing the execution of all the task's LUs.
The following diagram describes the main TDM task execution process on a task with tables only:

Click here for more information about task's tables handling.
checkMigrateAndUpdateTDMDB Job
This job runs every 10 seconds and checks the execution status of the running process. It selects records from the task_execution_list in the TDM DB table where the execution_status is running.
The execution status is being checked as follows:
- If the task contains selected tables to be processed - it checks the execution status of all related tables in task_exe_ref_stats in the TDM DB table.
- It checks the batch status based on the batch_id populated in task_execution_list.fabric_execution_id column by the tdmExecuteTask job.
When the process has been completed, the following TDM DB tables are updated by this job:
- task_execution_list, updates the execution_status and additional data.
- task_execution_entities, populates each entity or table and its status. Sets the id_type to ENTITY or REFERENCE according to the entity or to the table data type.
- task_exe_error_detailed, populates the execution errors in Extract tasks. Note that the execution errors of Load tasks are reported to this table by the PopulateTableErrors Actor.
A new Global has been added in TDM 8.1: TDM_BATCH_LIMIT. This Global enables limiting the number of entities to be populated into the TDM execution tables per task execution. From Fabric 7.2 onwards, it is possible to populate the LIMIT parameter of the batch_details command with -1 to get all batch's entities without a limit. Therefore, the TDM_BATCH_LIMIT Global is set to -1 by default, allowing to get all the batch's entities and populate them into the TDM DB during the task execution.
Handling Task Executions that have been Completed
A task execution is considered complete when it no longer has pending or running executions. The checkMigrateAndUpdateTDMDB job handles task executions that have been completed - as follows:
- It updates the execution summary in the TDM DB tables.
- It synchronizes the task execution details to Fabric: Each task execution is stored as an LUI in the TDM LU.
Updating the Task Executions Summary Table
Updates the following TDM DB table:
Syncing the Task Execution ID to TDM LU
The TDM LU holds the execution details of each task execution. The TDM's instance ID is the task_execution_id generated for each task execution.
A completed task execution is synchronized into the TDM LU. The execution information and the TDM execution reports are extracted from the TDM LUI data.




