Project Versioning
Implementing a Fabric project is an ongoing process that evolves in response to changing business needs. It is essential to manage the project's code in a source control system, such as GIT. Additionally, Fabric provides valuable features such as project version tagging, which enables visibility of the deployed version tag on the server. This capability grants greater control over your project's versions and allows for easy identification of the currently deployed version on a Fabric server.
The project versioning solution is built from 3 steps along the project lifecycle, helping you to control, verify, and have visibility of the project's version:
Tag a version, an action available within Studio.
Deploy Fabric objects tagged with a specific version to the server.
Check the project object version(s) in the Fabric console/terminal to understand what has been previously deployed.
Tag a Version
Studio helps you to tag a version by:
- Proposing the next version, according to the current version and based on semantic versioning format.
- Alerting you when local changes haven't been pushed to GIT.
- Alerting you when your changes are not aligned with other changes on your working GIT branch.
- Updating the project version in the project definitions and GIT as an annotated tag.
Version Tagging Workflow
The following is the recommended workflow:
Pull the project from GIT.
Develop and implement your code on the project.
Once the working phase is done, set a version for your work:
From the project tree root, right-click and choose 'Version Tag'.
The Version Tag pop-up window appears, displaying the information of the remote GIT branch, the proposed version tag, and an optional tag message. The proposed version is based on the previous version but can be changed, as described below.
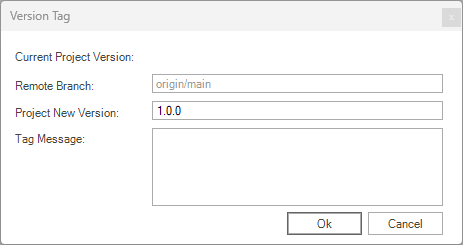
Please leave the new project version value, as suggested, or change it if needed.
Click OK to proceed.
Create a space based on a project from GIT.
Develop and implement your code on the project.
Once the working phase is done, set a version for your work:
From the top Fabric menu item, choose 'Version Tag'.
A pop-up window appears with information on the remote GIT branch, the proposed tag version, and an optional tag message. The proposed version is based on the previous version but can be changed, as described below.
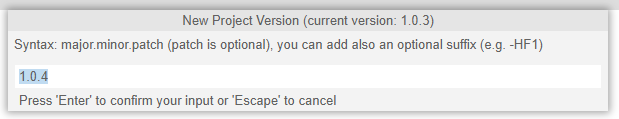
Please leave the new project version value, as suggested, or change it if needed.
Press 'Enter' to proceed.
Studio validation:
It checks that you do not have any local changes (no matter if committed locally or not) that are not pushed to GIT. If there are changes, Studio will warn you about them.
If you decide to create a version despite the warning, a version will be created containing only the pushed-to-GIT files.
It checks whether your changes are aligned with other changes on this GIT branch and warns you if they are not.
This case is valid: sometimes, two or more developers work on the same branch in parallel, on different capabilities, aimed at different phases. Thus, a version tag might contain specific developments made on that branch.
If you click to continue after examining the warnings (if any), the version tag is created in the project metadata file (.k2proj) and also as an annotated tag in GIT, where the tag message (if populated) is set. Both changes are committed and pushed into GIT.
Note: Studio is not responsible for the permissions a developer has to create a tag, nor from which branch it is allowed. The project owner needs to define it at GIT itself and define the procedures, for example, from which branch (e.g., any or specific "main") version tag to be produced.
Project Versioning Format
Following a semantic versioning structure is recommended, where a version number is built as MAJOR, MINOR, or PATCH, as defined here. Nevertheless, for simplicity, Studio enforces the format of X.Y, which starts with two digits and then allows you to decide how it will look.
The next time the version tagging action is initiated, Studio analyzes the current version and 'cleans' it from non-digit characters, preserving the convention used so far. For example, the next suggested version after "10.2.3-DEV-SNAPSHOT" will be "10.2.4," and the subsequent proposed version for "1.0-HF2" will be "1.1".
Deploying Tagged Objects
Fabric Studio allows the deployment of a project's objects to remote servers. As part of the project versioning capability, Studio allows you to decide, per remote server, whether to activate the version tag validation as a pre-deploy step. This ensures the most exact visibility of what is deployed at the target remote Fabric server.
In the Studio's User Preferences screen, you can choose, per remote server, in the Pre Deploy Tag Validation field, whether to skip it, warn when validation fails, or block deployment when validation fails.
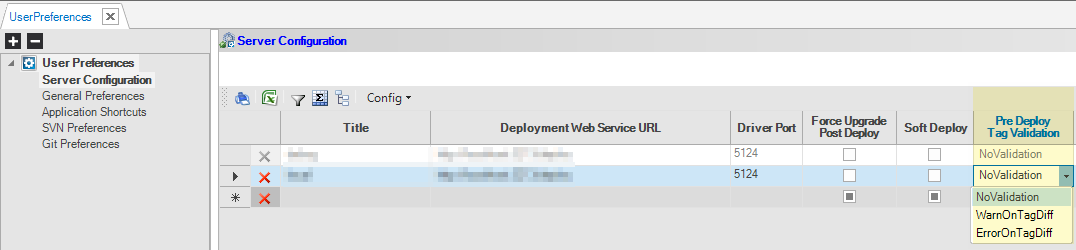
Upon deployment to a remote server, either the whole project or only specific objects, Studio performs the following according to the chosen preferences:
When NoValidation is chosen (default), Studio skips all tag checks. This is the less recommended option because if any local changes were done, they would not be reflected via the version command in the remote server. This option has been made available for customers that do not use the project versioning capability, and thus, as well as for backward compatibility, it is set as default.
When WarnOnTagDiff is chosen, Studio checks whether the candidates to be deployed are aligned with the version tag. This option compares the files due for deployment against the files in GIT by the current project version tag. If they are not equal - Studio warns you, but you can choose to continue anyway.
If you continue the deployment despite the warnings, a star will be added to the project's version in the built artifacts (e.g., "1.0.2*"). This will be used later on the remote server to indicate the
versioncommand results to hint to the user. By doing so, Studio empowers the version visibility in the remote target server about what is deployed.When ErrorOnTagDiff is chosen, Studio behaves similarly to the WarnOnTagDiff option, but in this case, it blocks the action, and deployment cannot be done.
When running Build Deploy Artifacts action, Studio behaves similarly, but without alerting the user as no deployment is done but building artifacts. Yet, when not skipping the validation checks, the built artifacts are signed with the star indication when not aligned with the tag. This means that later on, when these artifacts will be taken and deployed at another server using the offline deploy, the same indication will appear on the version command results, hinting users about.
Note: User preferences are saved on the developer's local machine's Studio, and thus, it is his responsibility to set the proper pre-deploy validation according to the project's procedures.
To use a specific version tag in a space, you must set it either at the project level (in a branch/tag field) or at the specific project space profile level.
Fabric commands
Fabric enables visibility on the version of the currently deployed objects in the server. By knowing the project version, you can examine - in GIT - the exact content of that object and, accordingly, better understand its functionality and behavior, especially if something doesn't work as expected.
- The
versioncommand shows, in addition to the product version, the project version for each LU, in a separate entry. Because each LU can be deployed separately, their versions may be different. For Example:
|Resource |Result |
+----------------+----------------------------------------+
|Version |7.2.0 |
|Full Version |7.2.0_37 |
|Version's commit|46a96b7246e96cecd84dfc3522302b99c7c1b65c|
|MDB Version |3.39.2 |
|Customer |1.0.0 |
|Orders |1.0.0 |
|Billing |1.0.3 |
Project version will not be shown as long as project versioning acts were not activated. Additionally, it will not be shown for LUs that haven't been deployed. This can also happen during the phase of starting using this capability, where some LUs are being deployed after using it will appear with the version, and others will not.
list wsandlist lutare also reflecting the project versioning, shown in the Project Version column in the command result.list wscommand result example:
|Name |Category|Version|Deployed |Project Version|
+-----+--------+-------+-----------------------+---------------+
|test1|test |1.0 |2023-06-01 12:23:30.608|1.0.0 |
|test2|test |1.0 |2023-07-03 18:27:49.738|1.0.3 |
list lut command result example:
|LU_NAME |Project Version|
+--------+---------------+
|Billing |1.0.3 |
|Customer|1.0.0 |
|Orders |1.0.0 |
- When the deployment was done, although it was not aligned with the tagged version, the
versioncommand yielded a star near the project version (e.g., "1.0.2*"), indicating that the deployed object is not equal to the version, but contain changes.
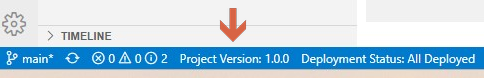
In Studio, you can see the currently deployed version also at the bottom status bar:
Notes
Using the project versioning capability is optional, and as long as it is not used, project metadata will not contain it. Thus, the version command will not show LU entries.
When the project's source code is not controlled in GIT, the related project versioning elements and actions will not be shown or acted upon.
If still needed, project version can be manually added to the k2proj.xml (at
<ProjectVersion>element), so that it will be reflected later in the version command result on the deployed server. As Studio validations cannot be run in such cases, there is no guarantee that the version shown in the version command's result really represents the version that was manually added and saved.A manual update shall not be done when working with GIT and the project version mechanism.

Project Versioning
Implementing a Fabric project is an ongoing process that evolves in response to changing business needs. It is essential to manage the project's code in a source control system, such as GIT. Additionally, Fabric provides valuable features such as project version tagging, which enables visibility of the deployed version tag on the server. This capability grants greater control over your project's versions and allows for easy identification of the currently deployed version on a Fabric server.
The project versioning solution is built from 3 steps along the project lifecycle, helping you to control, verify, and have visibility of the project's version:
Tag a version, an action available within Studio.
Deploy Fabric objects tagged with a specific version to the server.
Check the project object version(s) in the Fabric console/terminal to understand what has been previously deployed.
Tag a Version
Studio helps you to tag a version by:
- Proposing the next version, according to the current version and based on semantic versioning format.
- Alerting you when local changes haven't been pushed to GIT.
- Alerting you when your changes are not aligned with other changes on your working GIT branch.
- Updating the project version in the project definitions and GIT as an annotated tag.
Version Tagging Workflow
The following is the recommended workflow:
Pull the project from GIT.
Develop and implement your code on the project.
Once the working phase is done, set a version for your work:
From the project tree root, right-click and choose 'Version Tag'.
The Version Tag pop-up window appears, displaying the information of the remote GIT branch, the proposed version tag, and an optional tag message. The proposed version is based on the previous version but can be changed, as described below.

Please leave the new project version value, as suggested, or change it if needed.
Click OK to proceed.
Create a space based on a project from GIT.
Develop and implement your code on the project.
Once the working phase is done, set a version for your work:
From the top Fabric menu item, choose 'Version Tag'.
A pop-up window appears with information on the remote GIT branch, the proposed tag version, and an optional tag message. The proposed version is based on the previous version but can be changed, as described below.

Please leave the new project version value, as suggested, or change it if needed.
Press 'Enter' to proceed.
Studio validation:
It checks that you do not have any local changes (no matter if committed locally or not) that are not pushed to GIT. If there are changes, Studio will warn you about them.
If you decide to create a version despite the warning, a version will be created containing only the pushed-to-GIT files.
It checks whether your changes are aligned with other changes on this GIT branch and warns you if they are not.
This case is valid: sometimes, two or more developers work on the same branch in parallel, on different capabilities, aimed at different phases. Thus, a version tag might contain specific developments made on that branch.
If you click to continue after examining the warnings (if any), the version tag is created in the project metadata file (.k2proj) and also as an annotated tag in GIT, where the tag message (if populated) is set. Both changes are committed and pushed into GIT.
Note: Studio is not responsible for the permissions a developer has to create a tag, nor from which branch it is allowed. The project owner needs to define it at GIT itself and define the procedures, for example, from which branch (e.g., any or specific "main") version tag to be produced.
Project Versioning Format
Following a semantic versioning structure is recommended, where a version number is built as MAJOR, MINOR, or PATCH, as defined here. Nevertheless, for simplicity, Studio enforces the format of X.Y, which starts with two digits and then allows you to decide how it will look.
The next time the version tagging action is initiated, Studio analyzes the current version and 'cleans' it from non-digit characters, preserving the convention used so far. For example, the next suggested version after "10.2.3-DEV-SNAPSHOT" will be "10.2.4," and the subsequent proposed version for "1.0-HF2" will be "1.1".
Deploying Tagged Objects
Fabric Studio allows the deployment of a project's objects to remote servers. As part of the project versioning capability, Studio allows you to decide, per remote server, whether to activate the version tag validation as a pre-deploy step. This ensures the most exact visibility of what is deployed at the target remote Fabric server.
In the Studio's User Preferences screen, you can choose, per remote server, in the Pre Deploy Tag Validation field, whether to skip it, warn when validation fails, or block deployment when validation fails.

Upon deployment to a remote server, either the whole project or only specific objects, Studio performs the following according to the chosen preferences:
When NoValidation is chosen (default), Studio skips all tag checks. This is the less recommended option because if any local changes were done, they would not be reflected via the version command in the remote server. This option has been made available for customers that do not use the project versioning capability, and thus, as well as for backward compatibility, it is set as default.
When WarnOnTagDiff is chosen, Studio checks whether the candidates to be deployed are aligned with the version tag. This option compares the files due for deployment against the files in GIT by the current project version tag. If they are not equal - Studio warns you, but you can choose to continue anyway.
If you continue the deployment despite the warnings, a star will be added to the project's version in the built artifacts (e.g., "1.0.2*"). This will be used later on the remote server to indicate the
versioncommand results to hint to the user. By doing so, Studio empowers the version visibility in the remote target server about what is deployed.When ErrorOnTagDiff is chosen, Studio behaves similarly to the WarnOnTagDiff option, but in this case, it blocks the action, and deployment cannot be done.
When running Build Deploy Artifacts action, Studio behaves similarly, but without alerting the user as no deployment is done but building artifacts. Yet, when not skipping the validation checks, the built artifacts are signed with the star indication when not aligned with the tag. This means that later on, when these artifacts will be taken and deployed at another server using the offline deploy, the same indication will appear on the version command results, hinting users about.
Note: User preferences are saved on the developer's local machine's Studio, and thus, it is his responsibility to set the proper pre-deploy validation according to the project's procedures.
To use a specific version tag in a space, you must set it either at the project level (in a branch/tag field) or at the specific project space profile level.
Fabric commands
Fabric enables visibility on the version of the currently deployed objects in the server. By knowing the project version, you can examine - in GIT - the exact content of that object and, accordingly, better understand its functionality and behavior, especially if something doesn't work as expected.
- The
versioncommand shows, in addition to the product version, the project version for each LU, in a separate entry. Because each LU can be deployed separately, their versions may be different. For Example:
|Resource |Result |
+----------------+----------------------------------------+
|Version |7.2.0 |
|Full Version |7.2.0_37 |
|Version's commit|46a96b7246e96cecd84dfc3522302b99c7c1b65c|
|MDB Version |3.39.2 |
|Customer |1.0.0 |
|Orders |1.0.0 |
|Billing |1.0.3 |
Project version will not be shown as long as project versioning acts were not activated. Additionally, it will not be shown for LUs that haven't been deployed. This can also happen during the phase of starting using this capability, where some LUs are being deployed after using it will appear with the version, and others will not.
list wsandlist lutare also reflecting the project versioning, shown in the Project Version column in the command result.list wscommand result example:
|Name |Category|Version|Deployed |Project Version|
+-----+--------+-------+-----------------------+---------------+
|test1|test |1.0 |2023-06-01 12:23:30.608|1.0.0 |
|test2|test |1.0 |2023-07-03 18:27:49.738|1.0.3 |
list lut command result example:
|LU_NAME |Project Version|
+--------+---------------+
|Billing |1.0.3 |
|Customer|1.0.0 |
|Orders |1.0.0 |
- When the deployment was done, although it was not aligned with the tagged version, the
versioncommand yielded a star near the project version (e.g., "1.0.2*"), indicating that the deployed object is not equal to the version, but contain changes.
In Studio, you can see the currently deployed version also at the bottom status bar:

Notes
Using the project versioning capability is optional, and as long as it is not used, project metadata will not contain it. Thus, the version command will not show LU entries.
When the project's source code is not controlled in GIT, the related project versioning elements and actions will not be shown or acted upon.
If still needed, project version can be manually added to the k2proj.xml (at
<ProjectVersion>element), so that it will be reflected later in the version command result on the deployed server. As Studio validations cannot be run in such cases, there is no guarantee that the version shown in the version command's result really represents the version that was manually added and saved.A manual update shall not be done when working with GIT and the project version mechanism.