Secrets Management
A secret, such as a password, is considered sensitive data, and it is used in interfaces, Environments and Fabric System Database as a way to enable communication with external systems. Hence, secrets should be protected and suitably stored. Click here for further information about the secured storage of secrets in Fabric.
Fabric also supports integration with Secrets Management services, as they provide several benefits while secrets are not stored in Fabric itself, only their reference IDs are.
Secrets Management services are tools that aim to securely store, manage, access, and audit sensitive information such as passwords, API keys, and other credentials, across the organization. The features included in Secrets Management services are encryption, access controls, auditing, and automatic rotation of secrets.
Key advantages of Secrets Management services are:
- Reducing the risk of secret leaks when providing a secret for each client application.
- Having a single source of truth, which can be better controlled, changed, or rotated, manually or automatically.
- Managing access to secrets with fine-grained authorization policies.
- Detecting security breaches and unauthorized access attempts. This is achieved by analyzing audit logs and alerts, which provide a detailed history of client interactions that can also be used to guide security policy enforcement.
These are the Secrets Management service providers currently supported by Fabric, along with their official webpages:
- AWS Secrets Manager - AWS Secrets Manager
- HashiCorp Vault - HashiCorp Vault
- Azure Key Vault - Azure Key Vault
- CyberArk CCP - CyberArk CCP
- Google Cloud Secret Manager - Google Cloud Secret Manager
- One Identity Safeguard - One Identity Safeguard
How Does it Work
- The customer's security team administrator creates a set of credentials on either a database or a similarly secured resource server and then provisions them as secrets in the Secrets Management service. The latter encrypts and stores the credentials within the secrets.
- The administrator has to grant the Fabric (client application) permissions to access these secrets.
- When Fabric opens a connection to access the database/resource server via an interface, it examines whether its credentials are defined as reference IDs in an external Secrets Management service. If they are described as such, Fabric queries the Secrets Management service to retrieve the relevant secrets.
- The Secrets Management service decrypts and returns the secrets to Fabric over a secure channel.
- Fabric uses the secrets as the resource server credentials, as defined in the interface.
- Fabric caches the credentials in memory. If the connection to a resource server fails due to incorrect credentials, Fabric assumes that the credentials have been changed and therefore accesses the Secrets Management service again to retrieve them.
Using Secrets Management Services
To use a Secrets Management service, you should configure and set Fabric using the following two components:
- config.ini. Set the configuration in the config.ini file with the properties of the selected Secrets Management service, along with the access and permission details. Read here for more details.
- Interface Editor. Provision and mark the required interface connection details as those that should be taken from the Secrets Management service, as part of the project's implementation settings. Read here for more details.
Secrets Management
A secret, such as a password, is considered sensitive data, and it is used in interfaces, Environments and Fabric System Database as a way to enable communication with external systems. Hence, secrets should be protected and suitably stored. Click here for further information about the secured storage of secrets in Fabric.
Fabric also supports integration with Secrets Management services, as they provide several benefits while secrets are not stored in Fabric itself, only their reference IDs are.
Secrets Management services are tools that aim to securely store, manage, access, and audit sensitive information such as passwords, API keys, and other credentials, across the organization. The features included in Secrets Management services are encryption, access controls, auditing, and automatic rotation of secrets.
Key advantages of Secrets Management services are:
- Reducing the risk of secret leaks when providing a secret for each client application.
- Having a single source of truth, which can be better controlled, changed, or rotated, manually or automatically.
- Managing access to secrets with fine-grained authorization policies.
- Detecting security breaches and unauthorized access attempts. This is achieved by analyzing audit logs and alerts, which provide a detailed history of client interactions that can also be used to guide security policy enforcement.
These are the Secrets Management service providers currently supported by Fabric, along with their official webpages:
- AWS Secrets Manager - AWS Secrets Manager
- HashiCorp Vault - HashiCorp Vault
- Azure Key Vault - Azure Key Vault
- CyberArk CCP - CyberArk CCP
- Google Cloud Secret Manager - Google Cloud Secret Manager
- One Identity Safeguard - One Identity Safeguard
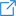
How Does it Work
- The customer's security team administrator creates a set of credentials on either a database or a similarly secured resource server and then provisions them as secrets in the Secrets Management service. The latter encrypts and stores the credentials within the secrets.
- The administrator has to grant the Fabric (client application) permissions to access these secrets.
- When Fabric opens a connection to access the database/resource server via an interface, it examines whether its credentials are defined as reference IDs in an external Secrets Management service. If they are described as such, Fabric queries the Secrets Management service to retrieve the relevant secrets.
- The Secrets Management service decrypts and returns the secrets to Fabric over a secure channel.
- Fabric uses the secrets as the resource server credentials, as defined in the interface.
- Fabric caches the credentials in memory. If the connection to a resource server fails due to incorrect credentials, Fabric assumes that the credentials have been changed and therefore accesses the Secrets Management service again to retrieve them.
Using Secrets Management Services
To use a Secrets Management service, you should configure and set Fabric using the following two components:
- config.ini. Set the configuration in the config.ini file with the properties of the selected Secrets Management service, along with the access and permission details. Read here for more details.
- Interface Editor. Provision and mark the required interface connection details as those that should be taken from the Secrets Management service, as part of the project's implementation settings. Read here for more details.