Fabric Commands
Fabric includes a number of commands for viewing Fabric configurations, updating Fabric settings and running Fabric processes. Fabric commands can be executed from either the Fabric console or via user code (project implementation) that invokes Fabric commands in the execute() and fetch() methods.
Note that Fabric commands are not case sensitive. For example, a Get, get, or GET command can be run.
Fabric Help
After logging in to Fabric, type help/Help/HELP to view a list of available Fabric commands. To view the description and syntax of a specific command, type help [command name].
For example:
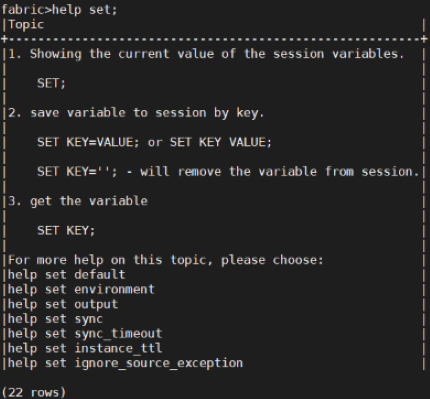
Fabric Commands - Main Groups
Fabric commands can be divided into the following groups:
|
Command Group |
Group Description |
|
|
Get an LUI into Fabric. |
|
Delete an LUI from Fabric. |
|
|
Detaches the LUI from the session for a list of LUs or for all LUs. |
|
|
View of the Fabric configurations and settings. |
|
|
|
Session and cluster levels settings. |
|
Fabric Security and Credentials
|
Set the Master Key for an LUI or the encryption details of an interface. Set users, roles, and permissions. |
|
|
Deploy and drop Fabric implementation commands. |
|
Fabric Environments and Interfaces
|
Deploy environments and test connections on an active environment. |
|
|
Run CQL queries on Cassandra. |
|
Fabric jobs execution and monitoring commands. |
|
|
Batch processing execution and monitoring commands. |
|
|
Check for running tasks and kill a task if needed. |
|
|
|
Trace Fabric operations and write the results to trace files. |
|
Commands for handling Reference tables. |
|
|
|
Support transactions to update LUI or Reference table data (Fabric as System of Record). |
|
Support Change Data Capture (CDC) across all LUI search functionalities. |
|
|
|
Run Broadway flow. |
|
|
Use EXPLAIN and EXPLAIN QUERY PLAN to analyze SQL queries on Fabric data. |
Get LUI Commands
Get Instance
The GET command is used to bring information for a given LUI and to synchronize information from data sources if needed.
Note that you can get LUIs from multiple LUs using one GET command, but you cannot get multiple LUIs from the same LU using one GET command. The following message is displayed when trying to get multiple LUIs from the same LU using one GET command:
Only single instance per LUT can be used on the same GET command.
It is possible to set the consistency level of the GET LUI command to ONE. If it fails to achieve a QUORUM consistency level, the sync mode is set to OFF. To do so, run the following Fabric command on the session:
- SET LUI_READ_ONE_WHEN_FAIL set =true
Note that this command sets the consistency level on the session level. The default value of this parameter is false.
The following table lists the GET commands:
|
Name |
Description |
Syntax |
Example |
GET |
Brings information for a specific LUI, or multiple LUIs of different LUs. Fabric checks if the LUI needs to be synced from the source system, syncs the LUI if needed, or brings the latest version of the LUI from Fabric.
|
Get an LUI: get <LUT_NAME>.'<INSTANCE_ID>'[@<DC>]; Get multiple instances of different LUs: get <LUT_NAME>.<INSTNACE_ID>'[@<DC>], <LUT_NAME_2>.<INSTNACE_ID>'[@<DC>]; |
get Customer.1; Get instance ID 1 of Customer LU. get Customer.1, CRM.34; Get instance ID 1 of Customer LU and instance ID 34 of CRM LU. |
GETF |
Brings information for a specific LUI, or multiple LUIs of different LUs. The instance is returned by an LUDB function.
|
Get an LUI: GETF <LUT_NAME>.<function name>(arg...)[@<DC>]; Get multiple instances of different LUs: GET <LUT_NAME>.<function name>(arg...)@<DC>,<LUT_NAME_2>.<function name>(arg...); |
getf Customer.fnCreateInstId(235); This function adds 1000 to the input value and returns the value 1235, Fabric gets Customer # 1235. |
USE |
USE command is an alias of GET command. |
Get an LUI: use <LUT_NAME>.'<INSTANCE_ID>'[@<DC>]; Get multiple instances of different LUs: use <LUT_NAME>.<INSTANCE_ID>'[@<DC>], <LUT_NAME_2>.<INSTANCE_ID>'[@<DC>]; |
use Customer.1; Get Instance ID 1 of Customer LU. use Customer.1, CRM.34; Get instance ID 1 of Customer LU and Instance ID 34 of CRM LU. |
Remote GET and GETF Commands
GET and GETF commands can be executed from a [datacenter (DC)]() that is not connected to data sources if other DCs are connected to the source interfaces. To do so, populate the DC parameter name of the GET and GETF commands to invoke the remote DC connected to the data source via the JDBC. The remote GET and GETF commands return the instances after executing the commands on the remote Fabric node. Cassandra then replicates the data between the nodes of the Cassandra cluster.
The remote GET and GETF commands run on a random Fabric node on the remote DC. Therefore, always verify the permissions for the GET and GETF commands’ execution on Fabric’s local and remote nodes.
Note that users are responsibile for identifying if a sync on an LUI is required, and to only then run the remote GET or GETF commands. This prevents unnecessary calls to the remote Fabric node and getting the local LUI version instead.
Delete LUI Command
The DELETE INSTANCE command deletes an LUI or multiple LUIs from Fabric.
Unlike the GET command, several LUI from the same LU can be deleted using one DELETE command.
The consistency level of delete instance is set in the LU_INSTANCE_DELETE parameter of the config.ini file. The default value is LOCAL_QUOROM.
The following table lists the DELETE commands:
|
Name |
Description |
Syntax |
Example |
DELETE INSTANCE |
Delete a specific LUI or a list of LUIs from Fabric.
|
Delete one instance: delete instance <LUT_Name>.'<instance_id>';Delete multiple instances: delete instance <LUT_Name>.'<instance_id>',<LUT_Name>.'<instance_id>',...; |
delete CRM.10; delete CRM.10, CRM.3; delete CRM.5, Customer.30; |
DELETE INSTANCES IF NOT EXIST |
Delete all LUIs that do not exist in the source system. To run this command, set the config.ini file as follows:
|
delete instances if not exist <LUT_Name>; |
delete instances if not exist CRM; |
Release LU
The Fabric RELEASE command is used to detach the LUI from the session on a list of LUs or all LUs.
Fabric View
Fabric has commands that display a Fabric configuration and its settings. For example:
Fabric cluster information:
- CLUSTERID, returns the cluster identifier defined on the node.id.
- CLUSTERSTATUS, returns the status of all Fabric nodes. Also includes: node_id, logical IDs, DC name, IP addresses.
- TIME, gets the node system time.
- VERSION INFO, the version of the installed Fabric. Note that to get the Fabric version when logged out of Fabric, use the k2fabric -version command.
Information about the deployed implementation:
- DESCRIBE, to query Fabric's metadata structure.
- LIST, a list of deployed objects and Fabric credentials (ROLES, USERS, TOKENS, ROLE_PERMISSIONS and METHODS).
General information:
- SET, displays the current session’s settings: Sync Mode, the LUI in the scope (the latest LUI, get on each LU), the deployed project name, Globals' values and the active environment.
Fabric Settings
Fabric Setting - Session Level
The Fabric SET command enables updating Fabric settings on a session level:
Set global variables.
Sync settings:
- Set sync mode.
- Set sync timeout.
- Set ignore source exception.
- Set always_sync
Set the active environment.
SET OUTPUT command, set the output format of query results.
SET INSTANCE_TTL command, set the time to live (TTL) in seconds for each LUI; the LUI is deleted automatically from Fabric after the TTL ends.
SET LUI_READ_ONE_WHEN_FAIL command, set the consistency level for the GET LUI command to ONE. If it fails to achieve a QUORUM consistency level, the sync mode is set to OFF.
Reset Session Level Setting
Use the following command to reset all the related parameters set on a session level to their default value: SET DEFAULT;
Fabric Setting - Cluster Level
Use the SET_GLOBAL command to set an active environment or a global value on a Fabric cluster.
The values are kept in the global_settings Cassandra table under k2system keyspace.
Fabric Security and Credentials
Fabric Security Commands
Master key generation commands used to encrypt LUI data and to encrypt an interface’s details.\ Click for more information about Fabric Security Hardening.
Fabric Credentials Commands, a list of commands for setting Fabric credentials like, users, roles, tokens or permissions.
Deploy and Drop Commands
Fabric commands to deploy Fabric implementation and Fabric Environments on the Fabric console.
Drop LU Command
The DROP LUTYPE command deletes LU metadata (LU schema) and its LUIs from Fabric. The DROP command also deletes the keyspace for the LU from Cassandra and the related LU entry from k2_lut_info in Cassandra. Once the LU is dropped it should be redeployed to the Fabric server.
Click for more information about Cassandra Keyspaces.
Note that this command is used mainly in a Testing environment to restart deployment configurations. In Production, the DROP LUTYPE command and reset.sh script are rarely used. A possible scenario is to clean the environment after a soft launch prior to starting an actual Production run. A Drop is followed by an initial load / migration of the data for the dropped LU.
Drop LU Syntax
DROP LUTYPE [LU Name];
Example:
DROP LUTYPE Customer;
Fabric Environments and Interfaces
Fabric enables the deployment of Fabric environments and setting active environments on session or cluster levels.
The DB interfaces of an active environment can be tested using the TEST_CONNECTION command. To do so, run the TEST_CONNECTION command without parameters to test the connection of all DB interfaces in the active environment.
Run Queries on Cassandra
CQL queries can be run on Cassandra in the Fabric server using the CQL command only for select statement.
Example:
fabric>cql select * from k2view_customer.entity;
Click for more information about Cassandra Basic Commands.
Jobs Commands
Get the Fabric jobs' list and status, start, stop, update and resume jobs.
Click for more information about Fabric jobs.
Batch Process Commands
The Batch process mechanism enables executing different types of Fabric commands in a batch mode on remote Fabric nodes.
Fabric has commands that start an execution, retry and cancel the execution of a batch process and commands that monitor an execution on batch processes in Fabric.
Note that MIGRATE commands are used as aliases to BATCH commands.
Click for more information about Fabric batch process mechanism.
Process Control
PS and Kill Commands
The PS command displays the current tasks running on the Fabric cluster, i.e. you can run this command on node1 and view tasks, running on node2. The PS command displays different types of tasks like Fabric commands, Fabric Jobs, Web Service and Graphit, Sync processes, Broadway Actor, parser, or User Logic. It displays the Node ID of each task.
The KILL command is used to kill any running task displayed by the PS command. Note that you can kill a task that runs on a different node on the Fabric cluster.
Execution Monitoring
The TRACE command enables tracing internal Fabric operations by request and writing them into Tracing files.
CommonDB & Reference Tables
Fabric enables creating Reference tables which can be used by all LUs or Web Services. A Reference table typically contains metadata. For example, a Postal Code table that identifies the postal code of customer addresses.
Reference table commands enable synchronizing, getting the sync status and waiting for sync processing of Reference tables to be completed before continuing the workflow.
Click for more information about Reference Tables.
Fabric Transactions
Fabric enables running a single transaction on a specific LU table of the Instance ID or on a Reference table. When this functionality is used, Fabric becomes the master of the data rather than syncing data from external systems. This way, Fabric can get transaction feeds and update a related Instance ID or Reference table accordingly. Always start a transaction with a *BEGIN* command before running INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE commands, and use COMMIT or ROLLBACK commands to commit or rollback the updates.
Fabric has a set of commands that support transactions:
- BEGIN, start a transaction.
- SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, and DELETE, run Select, Insert, Update and Delete transactions on the LUI or Reference table data.
- COMMIT and ROLLBACK, commit or rollback the updates.
Fabric also enables writing the transaction into a delta table using the SET ASYNC_TRX=true command.
Click for more information about Fabric Transactions.
CDC and Search
The Fabric Change Data Capture(CDC) solution notifies external systems about data changes and has built-in integration with Elasticsearch to enable a cross LUI search.
For example: search all customers called “John Doe” that live in “New-York”.
Fabric has a SEARCH command that initiates a search on Elasticsearch. In addition, the Fabric CDC_REPUBLISH_INSTANCE command can be used to republish CDC data on LUI.
Fabric Broadway
Fabric BROADWAY command runs a Broadway flow.
Queries Helpers
An SQL statement can be preceded by the EXPLAIN keyword or by the EXPLAIN QUERY PLAN phrase. The SQL statement then behaves like a query and returns information about the SQL statement’s operations if the EXPLAIN keyword or phrase is omitted.
EXPLAIN and EXPLAIN QUERY PLAN are intended for interactive analysis and troubleshooting only.
Example:
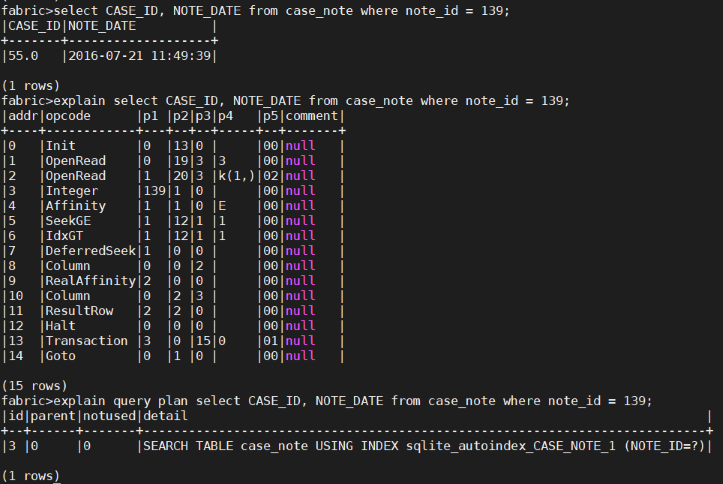
Fabric Commands
Fabric includes a number of commands for viewing Fabric configurations, updating Fabric settings and running Fabric processes. Fabric commands can be executed from either the Fabric console or via user code (project implementation) that invokes Fabric commands in the execute() and fetch() methods.
Note that Fabric commands are not case sensitive. For example, a Get, get, or GET command can be run.
Fabric Help
After logging in to Fabric, type help/Help/HELP to view a list of available Fabric commands. To view the description and syntax of a specific command, type help [command name].
For example:

Fabric Commands - Main Groups
Fabric commands can be divided into the following groups:
|
Command Group |
Group Description |
|
|
Get an LUI into Fabric. |
|
Delete an LUI from Fabric. |
|
|
Detaches the LUI from the session for a list of LUs or for all LUs. |
|
|
View of the Fabric configurations and settings. |
|
|
|
Session and cluster levels settings. |
|
Fabric Security and Credentials
|
Set the Master Key for an LUI or the encryption details of an interface. Set users, roles, and permissions. |
|
|
Deploy and drop Fabric implementation commands. |
|
Fabric Environments and Interfaces
|
Deploy environments and test connections on an active environment. |
|
|
Run CQL queries on Cassandra. |
|
Fabric jobs execution and monitoring commands. |
|
|
Batch processing execution and monitoring commands. |
|
|
Check for running tasks and kill a task if needed. |
|
|
|
Trace Fabric operations and write the results to trace files. |
|
Commands for handling Reference tables. |
|
|
|
Support transactions to update LUI or Reference table data (Fabric as System of Record). |
|
Support Change Data Capture (CDC) across all LUI search functionalities. |
|
|
|
Run Broadway flow. |
|
|
Use EXPLAIN and EXPLAIN QUERY PLAN to analyze SQL queries on Fabric data. |
Get LUI Commands
Get Instance
The GET command is used to bring information for a given LUI and to synchronize information from data sources if needed.
Note that you can get LUIs from multiple LUs using one GET command, but you cannot get multiple LUIs from the same LU using one GET command. The following message is displayed when trying to get multiple LUIs from the same LU using one GET command:
Only single instance per LUT can be used on the same GET command.
It is possible to set the consistency level of the GET LUI command to ONE. If it fails to achieve a QUORUM consistency level, the sync mode is set to OFF. To do so, run the following Fabric command on the session:
- SET LUI_READ_ONE_WHEN_FAIL set =true
Note that this command sets the consistency level on the session level. The default value of this parameter is false.
The following table lists the GET commands:
|
Name |
Description |
Syntax |
Example |
GET |
Brings information for a specific LUI, or multiple LUIs of different LUs. Fabric checks if the LUI needs to be synced from the source system, syncs the LUI if needed, or brings the latest version of the LUI from Fabric.
|
Get an LUI: get <LUT_NAME>.'<INSTANCE_ID>'[@<DC>]; Get multiple instances of different LUs: get <LUT_NAME>.<INSTNACE_ID>'[@<DC>], <LUT_NAME_2>.<INSTNACE_ID>'[@<DC>]; |
get Customer.1; Get instance ID 1 of Customer LU. get Customer.1, CRM.34; Get instance ID 1 of Customer LU and instance ID 34 of CRM LU. |
GETF |
Brings information for a specific LUI, or multiple LUIs of different LUs. The instance is returned by an LUDB function.
|
Get an LUI: GETF <LUT_NAME>.<function name>(arg...)[@<DC>]; Get multiple instances of different LUs: GET <LUT_NAME>.<function name>(arg...)@<DC>,<LUT_NAME_2>.<function name>(arg...); |
getf Customer.fnCreateInstId(235); This function adds 1000 to the input value and returns the value 1235, Fabric gets Customer # 1235. |
USE |
USE command is an alias of GET command. |
Get an LUI: use <LUT_NAME>.'<INSTANCE_ID>'[@<DC>]; Get multiple instances of different LUs: use <LUT_NAME>.<INSTANCE_ID>'[@<DC>], <LUT_NAME_2>.<INSTANCE_ID>'[@<DC>]; |
use Customer.1; Get Instance ID 1 of Customer LU. use Customer.1, CRM.34; Get instance ID 1 of Customer LU and Instance ID 34 of CRM LU. |
Remote GET and GETF Commands
GET and GETF commands can be executed from a [datacenter (DC)]() that is not connected to data sources if other DCs are connected to the source interfaces. To do so, populate the DC parameter name of the GET and GETF commands to invoke the remote DC connected to the data source via the JDBC. The remote GET and GETF commands return the instances after executing the commands on the remote Fabric node. Cassandra then replicates the data between the nodes of the Cassandra cluster.
The remote GET and GETF commands run on a random Fabric node on the remote DC. Therefore, always verify the permissions for the GET and GETF commands’ execution on Fabric’s local and remote nodes.
Note that users are responsibile for identifying if a sync on an LUI is required, and to only then run the remote GET or GETF commands. This prevents unnecessary calls to the remote Fabric node and getting the local LUI version instead.
Delete LUI Command
The DELETE INSTANCE command deletes an LUI or multiple LUIs from Fabric.
Unlike the GET command, several LUI from the same LU can be deleted using one DELETE command.
The consistency level of delete instance is set in the LU_INSTANCE_DELETE parameter of the config.ini file. The default value is LOCAL_QUOROM.
The following table lists the DELETE commands:
|
Name |
Description |
Syntax |
Example |
DELETE INSTANCE |
Delete a specific LUI or a list of LUIs from Fabric.
|
Delete one instance: delete instance <LUT_Name>.'<instance_id>';Delete multiple instances: delete instance <LUT_Name>.'<instance_id>',<LUT_Name>.'<instance_id>',...; |
delete CRM.10; delete CRM.10, CRM.3; delete CRM.5, Customer.30; |
DELETE INSTANCES IF NOT EXIST |
Delete all LUIs that do not exist in the source system. To run this command, set the config.ini file as follows:
|
delete instances if not exist <LUT_Name>; |
delete instances if not exist CRM; |
Release LU
The Fabric RELEASE command is used to detach the LUI from the session on a list of LUs or all LUs.
Fabric View
Fabric has commands that display a Fabric configuration and its settings. For example:
Fabric cluster information:
- CLUSTERID, returns the cluster identifier defined on the node.id.
- CLUSTERSTATUS, returns the status of all Fabric nodes. Also includes: node_id, logical IDs, DC name, IP addresses.
- TIME, gets the node system time.
- VERSION INFO, the version of the installed Fabric. Note that to get the Fabric version when logged out of Fabric, use the k2fabric -version command.
Information about the deployed implementation:
- DESCRIBE, to query Fabric's metadata structure.
- LIST, a list of deployed objects and Fabric credentials (ROLES, USERS, TOKENS, ROLE_PERMISSIONS and METHODS).
General information:
- SET, displays the current session’s settings: Sync Mode, the LUI in the scope (the latest LUI, get on each LU), the deployed project name, Globals' values and the active environment.
Fabric Settings
Fabric Setting - Session Level
The Fabric SET command enables updating Fabric settings on a session level:
Set global variables.
Sync settings:
- Set sync mode.
- Set sync timeout.
- Set ignore source exception.
- Set always_sync
Set the active environment.
SET OUTPUT command, set the output format of query results.
SET INSTANCE_TTL command, set the time to live (TTL) in seconds for each LUI; the LUI is deleted automatically from Fabric after the TTL ends.
SET LUI_READ_ONE_WHEN_FAIL command, set the consistency level for the GET LUI command to ONE. If it fails to achieve a QUORUM consistency level, the sync mode is set to OFF.
Reset Session Level Setting
Use the following command to reset all the related parameters set on a session level to their default value: SET DEFAULT;
Fabric Setting - Cluster Level
Use the SET_GLOBAL command to set an active environment or a global value on a Fabric cluster.
The values are kept in the global_settings Cassandra table under k2system keyspace.
Fabric Security and Credentials
Fabric Security Commands
Master key generation commands used to encrypt LUI data and to encrypt an interface’s details.\ Click for more information about Fabric Security Hardening.
Fabric Credentials Commands, a list of commands for setting Fabric credentials like, users, roles, tokens or permissions.
Deploy and Drop Commands
Fabric commands to deploy Fabric implementation and Fabric Environments on the Fabric console.
Drop LU Command
The DROP LUTYPE command deletes LU metadata (LU schema) and its LUIs from Fabric. The DROP command also deletes the keyspace for the LU from Cassandra and the related LU entry from k2_lut_info in Cassandra. Once the LU is dropped it should be redeployed to the Fabric server.
Click for more information about Cassandra Keyspaces.
Note that this command is used mainly in a Testing environment to restart deployment configurations. In Production, the DROP LUTYPE command and reset.sh script are rarely used. A possible scenario is to clean the environment after a soft launch prior to starting an actual Production run. A Drop is followed by an initial load / migration of the data for the dropped LU.
Drop LU Syntax
DROP LUTYPE [LU Name];
Example:
DROP LUTYPE Customer;
Fabric Environments and Interfaces
Fabric enables the deployment of Fabric environments and setting active environments on session or cluster levels.
The DB interfaces of an active environment can be tested using the TEST_CONNECTION command. To do so, run the TEST_CONNECTION command without parameters to test the connection of all DB interfaces in the active environment.
Run Queries on Cassandra
CQL queries can be run on Cassandra in the Fabric server using the CQL command only for select statement.
Example:
fabric>cql select * from k2view_customer.entity;
Click for more information about Cassandra Basic Commands.
Jobs Commands
Get the Fabric jobs' list and status, start, stop, update and resume jobs.
Click for more information about Fabric jobs.
Batch Process Commands
The Batch process mechanism enables executing different types of Fabric commands in a batch mode on remote Fabric nodes.
Fabric has commands that start an execution, retry and cancel the execution of a batch process and commands that monitor an execution on batch processes in Fabric.
Note that MIGRATE commands are used as aliases to BATCH commands.
Click for more information about Fabric batch process mechanism.
Process Control
PS and Kill Commands
The PS command displays the current tasks running on the Fabric cluster, i.e. you can run this command on node1 and view tasks, running on node2. The PS command displays different types of tasks like Fabric commands, Fabric Jobs, Web Service and Graphit, Sync processes, Broadway Actor, parser, or User Logic. It displays the Node ID of each task.
The KILL command is used to kill any running task displayed by the PS command. Note that you can kill a task that runs on a different node on the Fabric cluster.
Execution Monitoring
The TRACE command enables tracing internal Fabric operations by request and writing them into Tracing files.
CommonDB & Reference Tables
Fabric enables creating Reference tables which can be used by all LUs or Web Services. A Reference table typically contains metadata. For example, a Postal Code table that identifies the postal code of customer addresses.
Reference table commands enable synchronizing, getting the sync status and waiting for sync processing of Reference tables to be completed before continuing the workflow.
Click for more information about Reference Tables.
Fabric Transactions
Fabric enables running a single transaction on a specific LU table of the Instance ID or on a Reference table. When this functionality is used, Fabric becomes the master of the data rather than syncing data from external systems. This way, Fabric can get transaction feeds and update a related Instance ID or Reference table accordingly. Always start a transaction with a *BEGIN* command before running INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE commands, and use COMMIT or ROLLBACK commands to commit or rollback the updates.
Fabric has a set of commands that support transactions:
- BEGIN, start a transaction.
- SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, and DELETE, run Select, Insert, Update and Delete transactions on the LUI or Reference table data.
- COMMIT and ROLLBACK, commit or rollback the updates.
Fabric also enables writing the transaction into a delta table using the SET ASYNC_TRX=true command.
Click for more information about Fabric Transactions.
CDC and Search
The Fabric Change Data Capture(CDC) solution notifies external systems about data changes and has built-in integration with Elasticsearch to enable a cross LUI search.
For example: search all customers called “John Doe” that live in “New-York”.
Fabric has a SEARCH command that initiates a search on Elasticsearch. In addition, the Fabric CDC_REPUBLISH_INSTANCE command can be used to republish CDC data on LUI.
Fabric Broadway
Fabric BROADWAY command runs a Broadway flow.
Queries Helpers
An SQL statement can be preceded by the EXPLAIN keyword or by the EXPLAIN QUERY PLAN phrase. The SQL statement then behaves like a query and returns information about the SQL statement’s operations if the EXPLAIN keyword or phrase is omitted.
EXPLAIN and EXPLAIN QUERY PLAN are intended for interactive analysis and troubleshooting only.
Example:






