Cassandra Loader Architecture
Default Architecture
Custom Architecture
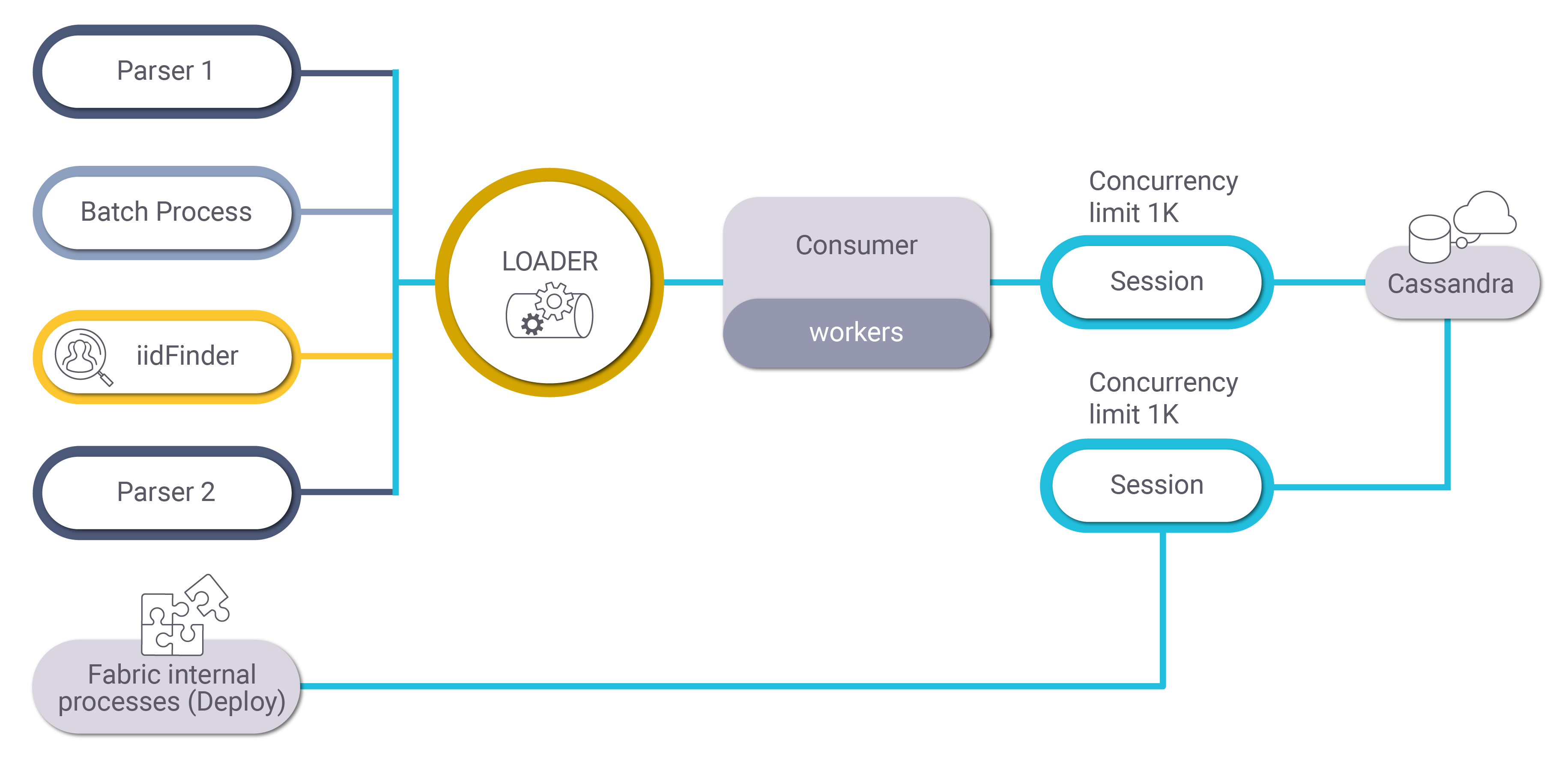
The default architecture defines two session objects, one used by loaders to perform WRITE operations to the Cassandra DB, and one used by internal Fabric processes like Deploy. The internal processes run on a separate session to prevent dependency on other heavy processes.
This architecture can be changed in the config.ini file to enable the loader to reach its optimal efficiency. The optimal configuration is based on a combination of effective hardware consumption and best possible performance.
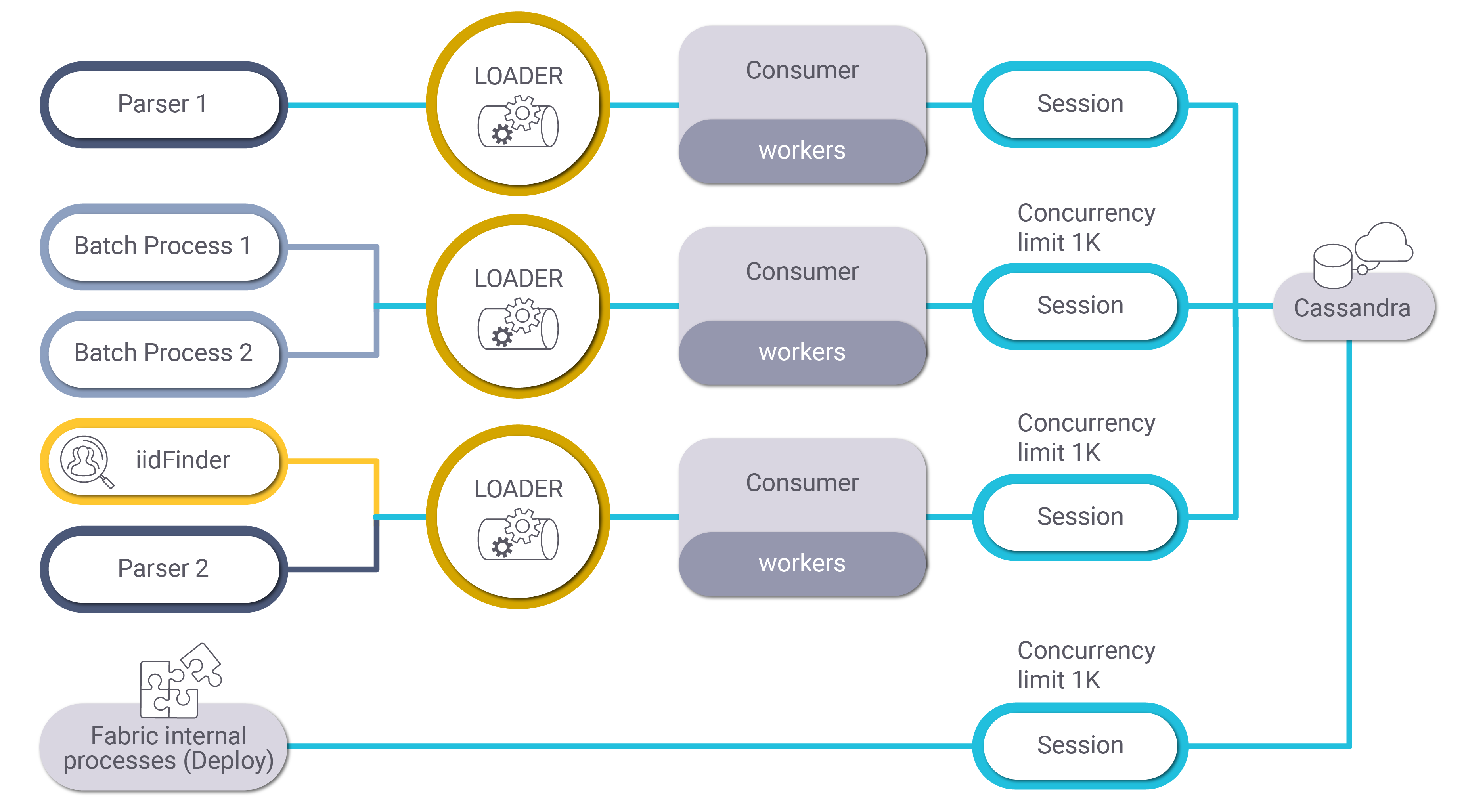
The configuration's parameters override the default settings, thus several loaders can be defined via the configuration, each in a separate session. For example, one loader per parser or separate loaders for parsers and for the iidFinder.
The concurrent number of messages to be sent to Cassandra by each session's object is set to a default value of 1K. The loader has a built-in queue management mechanism which adds a message in a queue if Cassandra reaches full capacity. The concurrency limit can be fine-tuned by the configuration's optimization process to a lower or higher number, while checking whether more load can be moved to Cassandra without causing the system to slow down or get stuck.
Cassandra Loader Architecture
Default Architecture

Custom Architecture

The default architecture defines two session objects, one used by loaders to perform WRITE operations to the Cassandra DB, and one used by internal Fabric processes like Deploy. The internal processes run on a separate session to prevent dependency on other heavy processes.
This architecture can be changed in the config.ini file to enable the loader to reach its optimal efficiency. The optimal configuration is based on a combination of effective hardware consumption and best possible performance.
The configuration's parameters override the default settings, thus several loaders can be defined via the configuration, each in a separate session. For example, one loader per parser or separate loaders for parsers and for the iidFinder.
The concurrent number of messages to be sent to Cassandra by each session's object is set to a default value of 1K. The loader has a built-in queue management mechanism which adds a message in a queue if Cassandra reaches full capacity. The concurrency limit can be fine-tuned by the configuration's optimization process to a lower or higher number, while checking whether more load can be moved to Cassandra without causing the system to slow down or get stuck.





