Web Service Properties
Fabric Web Services properties include definitions, methods, categories and essential metadata that contribute to the main functionalities and characteristics of the Web Service.
Web Service Properties are located on the top right corner of the Web Service window.
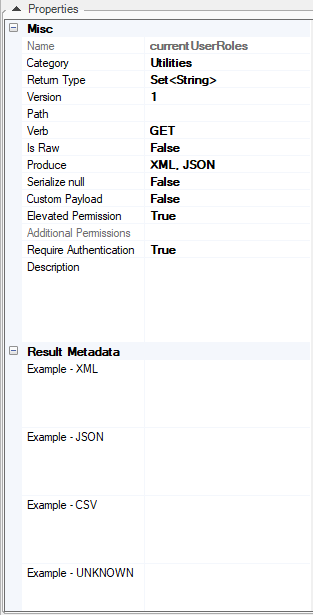
Web Services properties:
|
Property |
Description |
|
Name |
Name of the assigned web service function. The assigned name should be meaningful and should have a ws% prefix. |
|
Category |
Characteristics or class of the web service. Note that each category has a separate Java file. |
Return Type |
Type of Output value returned from the web service and displayed in a dropdown list, e.g., String, Long, Map, List, Customized Class or Object. These Output values can be overridden with new values. When sent as JSON, Fabric knows how to automatically serialize complex structures. |
Version |
Representation of the web service’s versioning control status. A version number is incorporated into the web service’s URL and is used to enable several web service versions. The default population of Version is 1. Versioning Logic
|
Path |
The URL path of a web service. This is the actual name to be used when external applications who use the web service call it. The URL path requires permissions and should be unique per each path/version/response format/request format.
For example, two web services sharing the same URL path:
For example: http://localhost:3213/api/v1/getCustomerInfo?token=t1&format=json&customerId=543; When this URL is called, Fabric invokes wsGetCustomerInfo. When the URL version is modified from v1 to v2, wsGetCustomerInfoDev is invoked. |
Verb |
Methods supported by the web service, as follows:
To select a method, click the dropdown list and enable it; at least one method should be selected. |
Is Raw |
Indicates whether the output structure should be manipulated automatically by Fabric. Values are either True or False. Default = False. When True, Fabric retrieves the data response as is, without parsing or formatting it, thus aligning it with the web service's output format. |
Produce |
Web Service’s output format. Default format: JSON Additional formats: XML, CSV. To select a format/s, click the dropdown menu and enable it/them. |
Serialize null |
If True, display fields with a null value in the response. Else, ignore fields with null values. The default is True. |
Custom Payload |
Indicates whether input parameters are automatically acquired by Fabric from the input stream as defined in the input parameters panel, or if it is to be implemented by the implementor manually. |
Elevated Permission |
Indicates if user permissions should be elevated to the Web Service. Default is set to False. For example, when set to False and the user role has no WRITE permissions, the user will not be able to write into Fabric using the Web Service. However when Elevated Permission is set to True on a Web Service, this restriction is dismissed. Added for Fabric V6.5.3Starting from Fabric V6.5.8, when a user role has a security profile that prevents him from accessing some LU tables, setting Elevated Permission to True dismisses this restriction.
|
Additional Permissions |
When an Elevated Permission is set to False, the developer might still wish that the web service caller will be able to activate certain methods, an act which is prohibited according to his role permissions. An example of such method is running a BATCH command. In such case, the developer can grant the caller the permission only for the web service session. To apply these permissions, the developer should specify what methods are allowed. At the Web Service Properties pane:
|
Require Authentication |
Indicates whether a web service requires authentication or not. Default is set to True. When set to False, it will allow calling the web service by skipping the Authentication step. This mode should be used carefully - use it only if a Web Service should be accessible for everyone, without enforcing an API key, a user/password, etc.Added for Fabric release 6.5.4 |
Description |
Web Service’s description on Swagger. |
Result Metadata |
Response example to be displayed in Swagger before the web service call. Set example-JSON, example-XML and example-CSV. |
How Do I Generate HTML Format or Legacy JSON/XML ?
To generate these formats, open the Java Logic file and add the following tag above the public class, which encapsulates the web services defined in the specific Logic category:
```java @legacy public class Logic extends WebServiceUserCode {…}
Then add the UNKNOWN value to the Produce function call in the line where the web service is defined:
java @webService(path = "test/getCustomerInfo", verb = {MethodType.GET, MethodType.POST, MethodType.PUT, MethodType.DELETE}, version = "1", isRaw = false, produce = {Produce.UNKNOWN})
Modify the Properties panel of the web service with Produce = "UNKNOWN" and Return Type = "Object".
After deploying the web service, call it from the browser using the appropriate token, parameter and format.
Example with HTML format:
html
http://localhost:3213/api/test/getCustomerInfo?ID=1000&token=tgreg&format=html
```
The response is displayed in the body of the browser's web page:
Web Service Properties
Fabric Web Services properties include definitions, methods, categories and essential metadata that contribute to the main functionalities and characteristics of the Web Service.
Web Service Properties are located on the top right corner of the Web Service window.

Web Services properties:
|
Property |
Description |
|
Name |
Name of the assigned web service function. The assigned name should be meaningful and should have a ws% prefix. |
|
Category |
Characteristics or class of the web service. Note that each category has a separate Java file. |
Return Type |
Type of Output value returned from the web service and displayed in a dropdown list, e.g., String, Long, Map, List, Customized Class or Object. These Output values can be overridden with new values. When sent as JSON, Fabric knows how to automatically serialize complex structures. |
Version |
Representation of the web service’s versioning control status. A version number is incorporated into the web service’s URL and is used to enable several web service versions. The default population of Version is 1. Versioning Logic
|
Path |
The URL path of a web service. This is the actual name to be used when external applications who use the web service call it. The URL path requires permissions and should be unique per each path/version/response format/request format.
For example, two web services sharing the same URL path:
For example: http://localhost:3213/api/v1/getCustomerInfo?token=t1&format=json&customerId=543; When this URL is called, Fabric invokes wsGetCustomerInfo. When the URL version is modified from v1 to v2, wsGetCustomerInfoDev is invoked. |
Verb |
Methods supported by the web service, as follows:
To select a method, click the dropdown list and enable it; at least one method should be selected. |
Is Raw |
Indicates whether the output structure should be manipulated automatically by Fabric. Values are either True or False. Default = False. When True, Fabric retrieves the data response as is, without parsing or formatting it, thus aligning it with the web service's output format. |
Produce |
Web Service’s output format. Default format: JSON Additional formats: XML, CSV. To select a format/s, click the dropdown menu and enable it/them. |
Serialize null |
If True, display fields with a null value in the response. Else, ignore fields with null values. The default is True. |
Custom Payload |
Indicates whether input parameters are automatically acquired by Fabric from the input stream as defined in the input parameters panel, or if it is to be implemented by the implementor manually. |
Elevated Permission |
Indicates if user permissions should be elevated to the Web Service. Default is set to False. For example, when set to False and the user role has no WRITE permissions, the user will not be able to write into Fabric using the Web Service. However when Elevated Permission is set to True on a Web Service, this restriction is dismissed. Added for Fabric V6.5.3Starting from Fabric V6.5.8, when a user role has a security profile that prevents him from accessing some LU tables, setting Elevated Permission to True dismisses this restriction.
|
Additional Permissions |
When an Elevated Permission is set to False, the developer might still wish that the web service caller will be able to activate certain methods, an act which is prohibited according to his role permissions. An example of such method is running a BATCH command. In such case, the developer can grant the caller the permission only for the web service session. To apply these permissions, the developer should specify what methods are allowed. At the Web Service Properties pane:
|
Require Authentication |
Indicates whether a web service requires authentication or not. Default is set to True. When set to False, it will allow calling the web service by skipping the Authentication step. This mode should be used carefully - use it only if a Web Service should be accessible for everyone, without enforcing an API key, a user/password, etc.Added for Fabric release 6.5.4 |
Description |
Web Service’s description on Swagger. |
Result Metadata |
Response example to be displayed in Swagger before the web service call. Set example-JSON, example-XML and example-CSV. |
How Do I Generate HTML Format or Legacy JSON/XML ?
To generate these formats, open the Java Logic file and add the following tag above the public class, which encapsulates the web services defined in the specific Logic category:
```java @legacy public class Logic extends WebServiceUserCode {…}
Then add the UNKNOWN value to the Produce function call in the line where the web service is defined:
java @webService(path = "test/getCustomerInfo", verb = {MethodType.GET, MethodType.POST, MethodType.PUT, MethodType.DELETE}, version = "1", isRaw = false, produce = {Produce.UNKNOWN})
Modify the Properties panel of the web service with Produce = "UNKNOWN" and Return Type = "Object".
After deploying the web service, call it from the browser using the appropriate token, parameter and format.
Example with HTML format:
html
http://localhost:3213/api/test/getCustomerInfo?ID=1000&token=tgreg&format=html
```
The response is displayed in the body of the browser's web page:




