Table Indexes
What Is an LU Table Index?
An index can be created for an LU table in order to improve performance when querying / updating LU tables in memory during the Sync process. Indexes are created on a table level and can be built for one or many fields. Each LU table can have several indexes where each index can contain several columns.
When Do I Create an Index?
When querying LU tables, indexes should be considered for fields used in WHERE clauses. Indexes should always be built in the same order as that of the conditions in the WHERE clause of the query. This also applies when using actions like Group By or Distinct which must be applied on indexed fields as displayed in Example 1. When an LU table is invoked as a Lookup table, create an index for the lookup input links which are used in the WHERE statement. It is recommended to create an index on the fields of a parent LU table which are used as a key to a child table within the LU Schema as displayed in Example 2.
Example 1 The USAGE table contains 100K records per customer. The SELECT SQL statement is:
SELECT sum (CALLS) from USAGE where TYPE = ‘I’ and PRIORITY = ‘High’
To improve the performance of this statement, a combined index should be created for the TYPE and PRIORITY columns, where TYPE is the first column in the index and PRIORITY is the second.
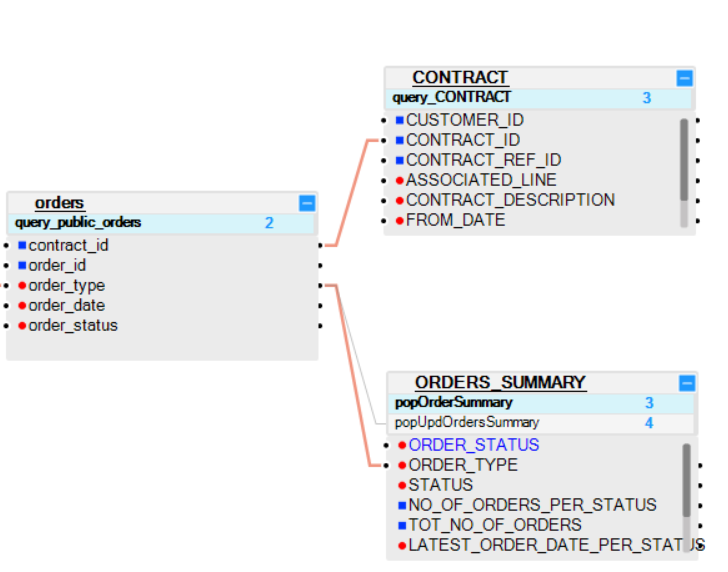
Example 2 The ORDERS table is a parent table of the CONTRACT and ORDERS_SUMMARY tables:
- The CONTRACT table is linked to the ORDERS table via the CONTRACT_ID field.
- The ORDERS_SUMMARY table is linked to the ORDERS table via the ORDER_TYPE field. It is therefore recommended to create two indexes for the ORDERS table:
- One for the CONTRACT_ID field.
- One for the ORDER_TYPE field.
Index Definition
LU table indexes are defined in the Indexes Tab in the Table window where they can also be added, modified or removed from a table. The following Index settings can be defined:
How Do I Add an Index?
- Go to Project Tree > Logical Units > [LU Name] > Tables > double click [Table Name] to open the table’s settings.
- In the Columns tab, right click one or more fields and select Create Index from Selected Columns.
- Click the Indexes tab to display a list of indexes.
- Check / uncheck PK and Unique to complete the index definition.
- Save the table.
How Do I Delete an Index?
- Go to Project Tree > Logical Units > [LU Name] > Tables > double click [Table Name] to open the table’s settings.
- In the Indexes tab, click Delete to delete the index.
How Do I Get a List of Indexes?
The DESCRIBE command is one of Fabric View commands and it is used to query the Fabric metadata structure on a deployed project in the Fabric console. For example, before performing a SELECT SQL query in the Web Service to get the list of indexes. To get the list of indexes for a specified table, use one of the following commands.
Syntax:
DESCRIBE INDEX; Get all system indexes.
DESCRIBE INDEX LU Name.Table Name Get the indexes of a specific table within the LU name.;
DESCRIBE INDEX customer; Get all indexes of the schema of LU Customer.
DESCRIBE INDEX customer.address_billing; Get the indexes of a specific table within the Customer Schema.
DESCRIBE INDEX customer.address%; Get the indexes of all tables starting with address.
Table Indexes
What Is an LU Table Index?
An index can be created for an LU table in order to improve performance when querying / updating LU tables in memory during the Sync process. Indexes are created on a table level and can be built for one or many fields. Each LU table can have several indexes where each index can contain several columns.
When Do I Create an Index?
When querying LU tables, indexes should be considered for fields used in WHERE clauses. Indexes should always be built in the same order as that of the conditions in the WHERE clause of the query. This also applies when using actions like Group By or Distinct which must be applied on indexed fields as displayed in Example 1. When an LU table is invoked as a Lookup table, create an index for the lookup input links which are used in the WHERE statement. It is recommended to create an index on the fields of a parent LU table which are used as a key to a child table within the LU Schema as displayed in Example 2.
Example 1 The USAGE table contains 100K records per customer. The SELECT SQL statement is:
SELECT sum (CALLS) from USAGE where TYPE = ‘I’ and PRIORITY = ‘High’
To improve the performance of this statement, a combined index should be created for the TYPE and PRIORITY columns, where TYPE is the first column in the index and PRIORITY is the second.
Example 2 The ORDERS table is a parent table of the CONTRACT and ORDERS_SUMMARY tables:
- The CONTRACT table is linked to the ORDERS table via the CONTRACT_ID field.
- The ORDERS_SUMMARY table is linked to the ORDERS table via the ORDER_TYPE field. It is therefore recommended to create two indexes for the ORDERS table:
- One for the CONTRACT_ID field.
- One for the ORDER_TYPE field.

Index Definition
LU table indexes are defined in the Indexes Tab in the Table window where they can also be added, modified or removed from a table. The following Index settings can be defined:
How Do I Add an Index?
- Go to Project Tree > Logical Units > [LU Name] > Tables > double click [Table Name] to open the table’s settings.
- In the Columns tab, right click one or more fields and select Create Index from Selected Columns.
- Click the Indexes tab to display a list of indexes.
- Check / uncheck PK and Unique to complete the index definition.
- Save the table.
How Do I Delete an Index?
- Go to Project Tree > Logical Units > [LU Name] > Tables > double click [Table Name] to open the table’s settings.
- In the Indexes tab, click Delete to delete the index.
How Do I Get a List of Indexes?
The DESCRIBE command is one of Fabric View commands and it is used to query the Fabric metadata structure on a deployed project in the Fabric console. For example, before performing a SELECT SQL query in the Web Service to get the list of indexes. To get the list of indexes for a specified table, use one of the following commands.
Syntax:
DESCRIBE INDEX; Get all system indexes.
DESCRIBE INDEX LU Name.Table Name Get the indexes of a specific table within the LU name.;
DESCRIBE INDEX customer; Get all indexes of the schema of LU Customer.
DESCRIBE INDEX customer.address_billing; Get the indexes of a specific table within the Customer Schema.
DESCRIBE INDEX customer.address%; Get the indexes of all tables starting with address.




