Parser Actors
Broadway has a parsers category of Actors. These Actors can parse input streams into different formats like JSON, CSV and XML.
When reading an input stream, the Actors can parse it into valid objects based on the specific delimiters of each input format while holding only one object in the memory at a time. This article describes these Actors and how to work with them.
JsonParser Actor
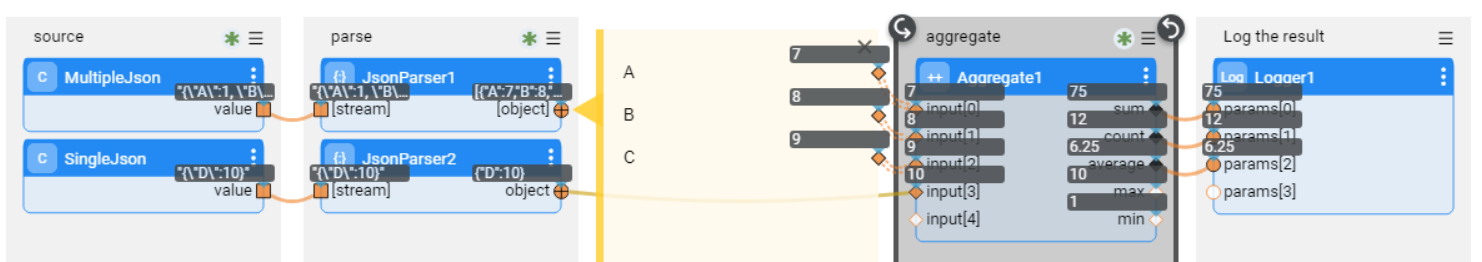
The JsonParser Actor analyzes input streams, represented by an iterable collection of blobs or strings, and returns a collection of the JSON objects found in the stream. If the single input attribute is set to True, the Actor expects only a single object in the input stream. Otherwise, the Actor can handle input streams with multiple JSON objects.
The json.flow example shows how the JsonParser Actor handles two types of inputs - a single JSON object and one with multiple objects.
Click Actions > Examples in the Main menu to open the json.flow example.
CsvParser Actor
The CsvParser Actor analyzes an input stream and returns an array of objects whereby each array row is a row of the input CSV stream. The Actor runs until it detects the end of the stream.
If the header input argument is set to True, the Actor uses the first row as a header row. In this case, the labels in the header are used to mark the row object.
Parser Actors are usually followed by an iteration that allow iterating over each row in the Actor's output object consecutively.
CsvParser Flow Example
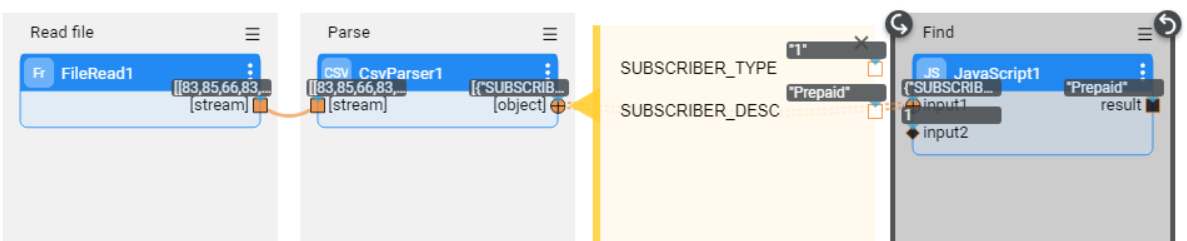
The following example shows how to find a subscriber description by the given subscriber type. This is done by providing the subscriber type as an external input argument, then reading and parsing a CSV file which has a list of types and their description.
The parser processes the file's rows consecutively by validating the data in the Find Stage using the JavaScript Actor's code via access to the flowArgs arguments and the contextLoop object. When the required given subscriber type is found, the iteration stops, and the flow returns the description.
if (input1.SUBSCRIBER_TYPE == flowArgs["input_subs_type"]) {
contextLoop.stop();
input1.SUBSCRIBER_DESC;
}
XmlParser and XmlParserLegacy Actors
The XmlParser Actor analyzes an input stream and outputs the objects found in the stream.
Starting from Fabric 6.5.3, there are two XMLParser Actors:
- The existing XmlParser Actor has been renamed to XMLParserLegacy. It supports parsing an XML with a list of objects only, without attributes.
- The new XMLParser supports parsing an XML with a list of objects that can include attributes. And example of an XML that can be parsed by XmlParser Actor is shown below:
<office name="New York">
<user id="1" name="John" last_name="Wick">
<room>123</room>
<phone_number>987654321</phone_number>
<phone_number>123456789</phone_number>
</user>
<user id="2" name="Alice" last_name="Liddell">
<room>wonderland</room>
<phone_number>3334445555</phone_number>
<phone_number>7776667777</phone_number>
</user>
</office>
The enhanced functionality of the XMLParser Actor is that it enables setting an object name to the parsed XML elements and parsed attributes using its new input arguments valueField and attributesField.
- The input arguments valueField and attributesField have default values that can be changed or set to null.
- There can be four combinations of setting the input arguments valueField and attributesField.
- Both valueField and attributesField have values, either the default values ('_value' and '__attributes') or the updated ones.
- One of the arguments have a value while another one is empty.
- Both of the arguments are empty.
- As a result of how these input arguments are set, there can be four different structures of the output object.
- When an XML includes an element with attributes and a primitive value (not a nested XML element), setting valueField to null (empty value) is not supported.
In addition, the enhanced XMLParser Actor enables determining if namespace information is added to the object by setting the input argument namespaces to true.
Example of a parsed object when valueField = '_value' and attributesField = '__attributes'
{
"office": {
"_attributes": {
"name": "New York"
},
"_value": {
"user": [{
"_attributes": {
"name": "John",
"last_name": "Wick",
"id": "1"
},
"_value": {
"room": {
"_value": "123"
},
"phone_number": [{
"_value": "987654321"
}, {
"_value": "123456789"
}
]
}
}, {
"_attributes": {
"name": "Alice",
"last_name": "Liddell",
"id": "2"
},
"_value": {
"room": {
"_value": "wonderland"
},
"phone_number": [{
"_value": "3334445555"
}, {
"_value": "7776667777"
}
]
}
}
]
}
}
}
Example of a parsed object when valueField = '_value' and attributesField is empty
{
"office": {
"name": "New York",
"_value": {
"user": [
{
"name": "John",
"last_name": "Wick",
"id": "1",
"_value": {
"room": {
"_value": "123"
},
"phone_number": [
{
"_value": "987654321"
},
{
"_value": "123456789"
}
]
}
},
{
"name": "Alice",
"last_name": "Liddell",
"id": "2",
"_value": {
"room": {
"_value": "wonderland"
},
"phone_number": [
{
"_value": "3334445555"
},
{
"_value": "7776667777"
}
]
}
}
]
}
}
}
Example of a parsed object when both valueField and attributesField are empty
{
"name": "New York",
"office": {
"name": "John",
"last_name": "Wick",
"id": "1",
"user": [
{
"room": "123",
"phone_number": [
"987654321",
"123456789"
]
},
{
"room": "wonderland",
"phone_number": [
"3334445555",
"7776667777"
]
}
]
}
}
Starting from Fabric 6.5.4, the XMLParser Actor provides an ability to iterate on the XML elements. This feature enables handling large XML files without loading full XML to memory. To do so, set the skipRoot input argument to true and connect the input stream using an Iterate link type. Then the root is skipped and the Actor returns a stream of elements.
Other Supported Parsers
Additional parser Actors supported by Broadway are:
- Base64Decode / Base64Encode Actor - analyzes an input, and outputs it as an encoded string or a decoded buffer.
- FixedColumnParser Actor - traverses an incoming stream, and for each line parses the columns using their fixed position in the line.
- LinesParser Actor - traverses an incoming stream, and outputs individual lines.
The Actor's description includes the detailed explanation of the Actor's capabilities. Click 
Checkout xml.flow for the XmlParser example and lines.flow for the LinesParser example. To do so, go to Actions > Examples in the Main menu.
Parser Actors
Broadway has a parsers category of Actors. These Actors can parse input streams into different formats like JSON, CSV and XML.
When reading an input stream, the Actors can parse it into valid objects based on the specific delimiters of each input format while holding only one object in the memory at a time. This article describes these Actors and how to work with them.
JsonParser Actor
The JsonParser Actor analyzes input streams, represented by an iterable collection of blobs or strings, and returns a collection of the JSON objects found in the stream. If the single input attribute is set to True, the Actor expects only a single object in the input stream. Otherwise, the Actor can handle input streams with multiple JSON objects.
The json.flow example shows how the JsonParser Actor handles two types of inputs - a single JSON object and one with multiple objects.
Click Actions > Examples in the Main menu to open the json.flow example.
CsvParser Actor
The CsvParser Actor analyzes an input stream and returns an array of objects whereby each array row is a row of the input CSV stream. The Actor runs until it detects the end of the stream.
If the header input argument is set to True, the Actor uses the first row as a header row. In this case, the labels in the header are used to mark the row object.
Parser Actors are usually followed by an iteration that allow iterating over each row in the Actor's output object consecutively.
CsvParser Flow Example
The following example shows how to find a subscriber description by the given subscriber type. This is done by providing the subscriber type as an external input argument, then reading and parsing a CSV file which has a list of types and their description.
The parser processes the file's rows consecutively by validating the data in the Find Stage using the JavaScript Actor's code via access to the flowArgs arguments and the contextLoop object. When the required given subscriber type is found, the iteration stops, and the flow returns the description.
if (input1.SUBSCRIBER_TYPE == flowArgs["input_subs_type"]) {
contextLoop.stop();
input1.SUBSCRIBER_DESC;
}
XmlParser and XmlParserLegacy Actors
The XmlParser Actor analyzes an input stream and outputs the objects found in the stream.
Starting from Fabric 6.5.3, there are two XMLParser Actors:
- The existing XmlParser Actor has been renamed to XMLParserLegacy. It supports parsing an XML with a list of objects only, without attributes.
- The new XMLParser supports parsing an XML with a list of objects that can include attributes. And example of an XML that can be parsed by XmlParser Actor is shown below:
<office name="New York">
<user id="1" name="John" last_name="Wick">
<room>123</room>
<phone_number>987654321</phone_number>
<phone_number>123456789</phone_number>
</user>
<user id="2" name="Alice" last_name="Liddell">
<room>wonderland</room>
<phone_number>3334445555</phone_number>
<phone_number>7776667777</phone_number>
</user>
</office>
The enhanced functionality of the XMLParser Actor is that it enables setting an object name to the parsed XML elements and parsed attributes using its new input arguments valueField and attributesField.
- The input arguments valueField and attributesField have default values that can be changed or set to null.
- There can be four combinations of setting the input arguments valueField and attributesField.
- Both valueField and attributesField have values, either the default values ('_value' and '__attributes') or the updated ones.
- One of the arguments have a value while another one is empty.
- Both of the arguments are empty.
- As a result of how these input arguments are set, there can be four different structures of the output object.
- When an XML includes an element with attributes and a primitive value (not a nested XML element), setting valueField to null (empty value) is not supported.
In addition, the enhanced XMLParser Actor enables determining if namespace information is added to the object by setting the input argument namespaces to true.
Example of a parsed object when valueField = '_value' and attributesField = '__attributes'
{
"office": {
"_attributes": {
"name": "New York"
},
"_value": {
"user": [{
"_attributes": {
"name": "John",
"last_name": "Wick",
"id": "1"
},
"_value": {
"room": {
"_value": "123"
},
"phone_number": [{
"_value": "987654321"
}, {
"_value": "123456789"
}
]
}
}, {
"_attributes": {
"name": "Alice",
"last_name": "Liddell",
"id": "2"
},
"_value": {
"room": {
"_value": "wonderland"
},
"phone_number": [{
"_value": "3334445555"
}, {
"_value": "7776667777"
}
]
}
}
]
}
}
}
Example of a parsed object when valueField = '_value' and attributesField is empty
{
"office": {
"name": "New York",
"_value": {
"user": [
{
"name": "John",
"last_name": "Wick",
"id": "1",
"_value": {
"room": {
"_value": "123"
},
"phone_number": [
{
"_value": "987654321"
},
{
"_value": "123456789"
}
]
}
},
{
"name": "Alice",
"last_name": "Liddell",
"id": "2",
"_value": {
"room": {
"_value": "wonderland"
},
"phone_number": [
{
"_value": "3334445555"
},
{
"_value": "7776667777"
}
]
}
}
]
}
}
}
Example of a parsed object when both valueField and attributesField are empty
{
"name": "New York",
"office": {
"name": "John",
"last_name": "Wick",
"id": "1",
"user": [
{
"room": "123",
"phone_number": [
"987654321",
"123456789"
]
},
{
"room": "wonderland",
"phone_number": [
"3334445555",
"7776667777"
]
}
]
}
}
Starting from Fabric 6.5.4, the XMLParser Actor provides an ability to iterate on the XML elements. This feature enables handling large XML files without loading full XML to memory. To do so, set the skipRoot input argument to true and connect the input stream using an Iterate link type. Then the root is skipped and the Actor returns a stream of elements.
Other Supported Parsers
Additional parser Actors supported by Broadway are:
- Base64Decode / Base64Encode Actor - analyzes an input, and outputs it as an encoded string or a decoded buffer.
- FixedColumnParser Actor - traverses an incoming stream, and for each line parses the columns using their fixed position in the line.
- LinesParser Actor - traverses an incoming stream, and outputs individual lines.
The Actor's description includes the detailed explanation of the Actor's capabilities. Click 
Checkout xml.flow for the XmlParser example and lines.flow for the LinesParser example. To do so, go to Actions > Examples in the Main menu.