Amazon S3 Storage Interface
The Amazon S3 Storage interface type is used to define the connections between S3 bucket and a data stream.
When creating an Interface Listener for a Broadway flow, an Amazon S3 Storage interface is required to detect new files added to S3.
Authentication
The AWS S3 interface supports two modes of authentication: 1) use of an Access Key and Secret Access Key, and 2) short-lived credentials using AWS STS and IRSA.
To learn how Fabric leverages AWS STS and IRSA, please refer to the How Fabric Leverages AWS IAM in a Kubernetes Environment article.
Creating the Interface
To create a new Amazon S3 Storage interface, do the following:
Go to Project Tree > Shared Objects, right click Interfaces, select New Interface and then select Amazon S3 Storage from the File System section to open the New Interface window.
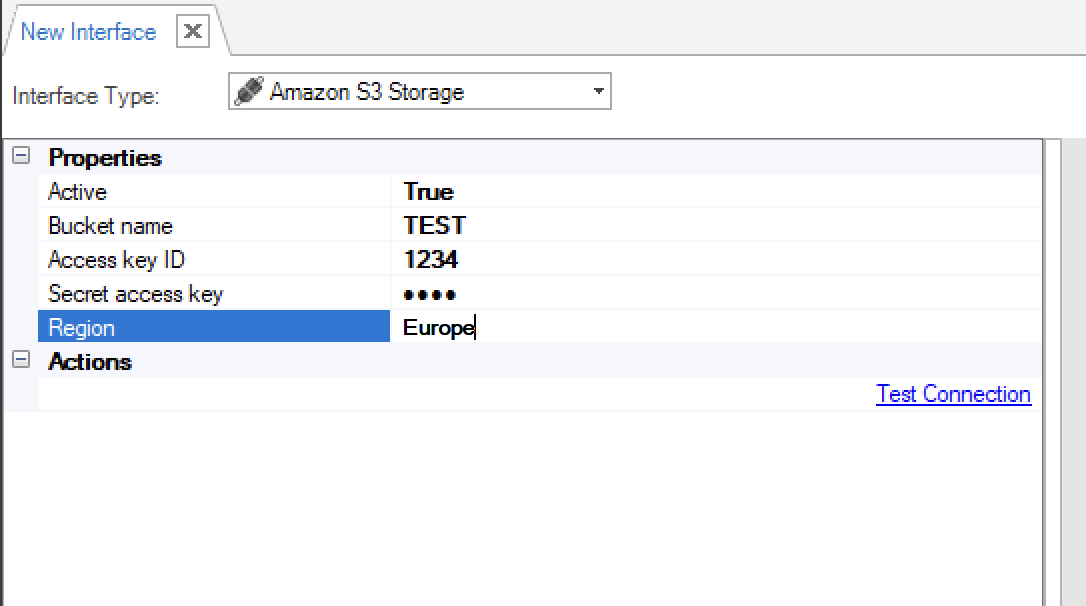
Populate the connection's settings and click Save.
Go to Project Tree > Shared Objects, right click Interfaces, select New Interface and then select Amazon S3 Storage from the Interface Type dropdown menu to open the New Interface window.
Enter a suitable name for your new Amazon S3 Storage Interface, then click Create
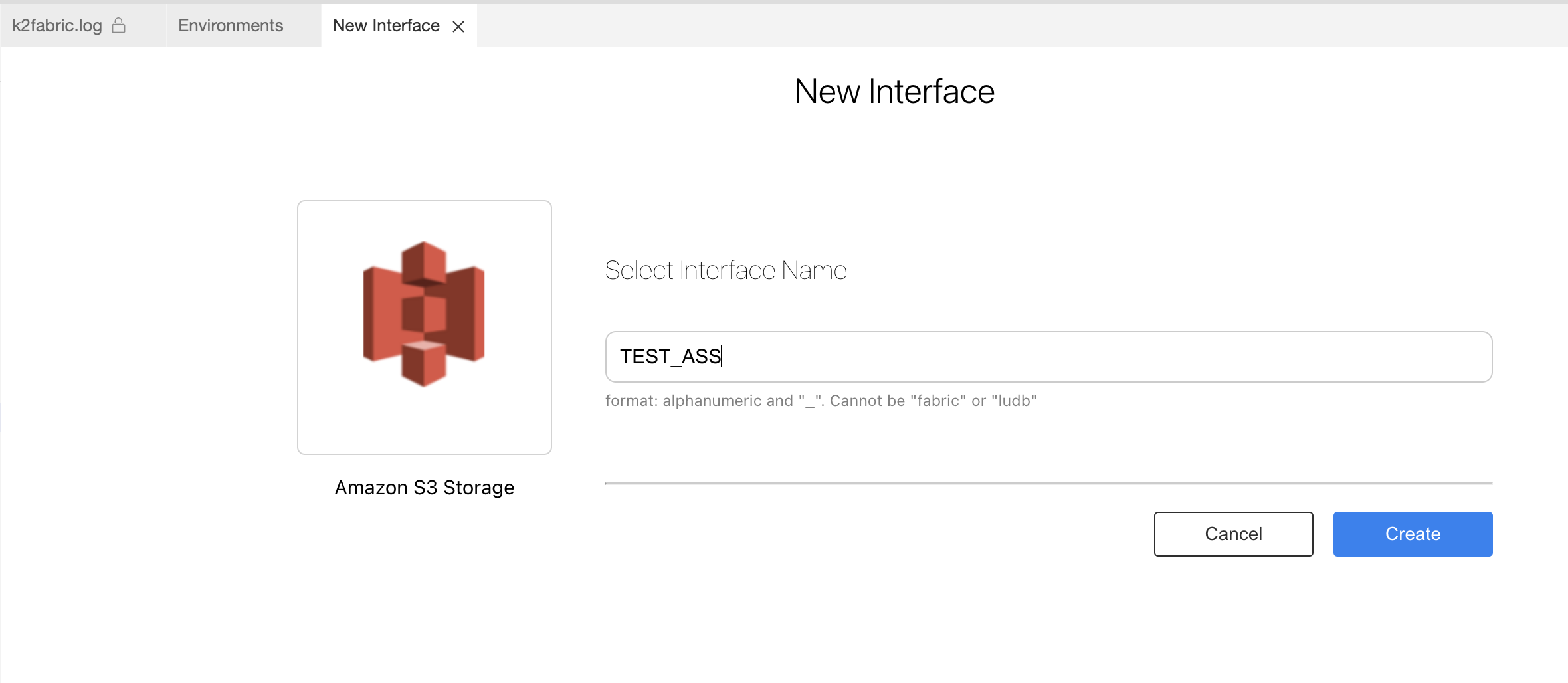
Populate the connection's settings and click Save.
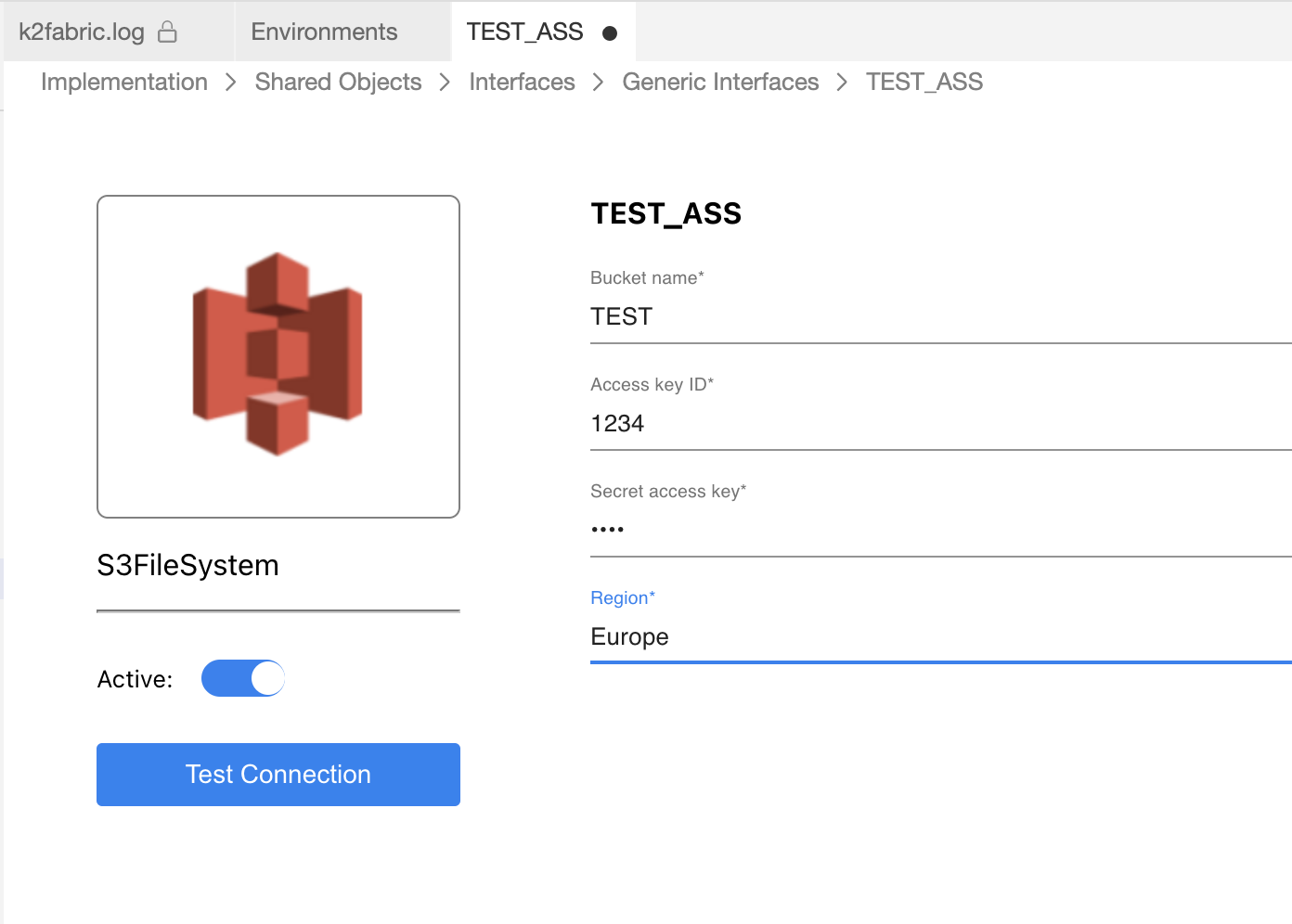
If the interface is supposed to be used for File Cataloging, expand the Discovery section and populate the names of 3 Broadway flows. This option is available starting from Fabric V8.3. Click here for more information about the File Cataloging solution.
Connection Settings
Click for more information about the File Cataloging solution.
Example of Using an Amazon S3 Storage Interface
To create an Interface Listener that runs on an S3 interface, do the following:
Create an interface using an Amazon S3 Storage interface type.
Create a Broadway flow either under Shared Objects or under the same Logical Unit. The flow reads data from a file using the predefined interface and populates it into the DB.
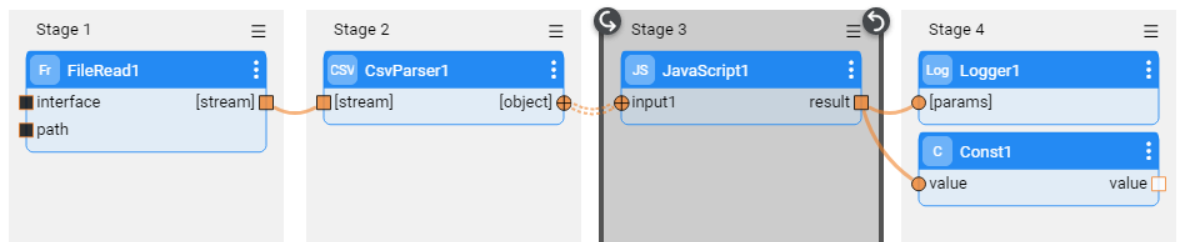
- Note that the interface and the path input arguments of the FileRead Actor are defined as External link type. Their values are passed from the defined interface by the Listener.
Add an InterfaceListener Actor to the "deploy.flow" flow, located at the Broadway folder. Use the Broadway flow, which you created in the previous step, as the
flowNameproperty in this actor.Deploy the LU to activate the Listener.
Using the InterfaceListener Actor
The InterfaceListener Actor enables the flow in which it is instantiated to listen to Amazon S3 Storage interface and trigger another Broadway flow upon arrival of a new file on the interface.
To create an Interface Listener job from a Broadway flow, add the InterfaceListener Actor to the flow.
Fill in the following parameters in the Actor's Properties tab:
flowName, the flow to be triggered by the Interface Listener.
interfaceName, the interface that is being listened and used to trigger the flow defined above, once a new file is detected on the file system to which the interface points.
affinity, sets which node/DC name IP address is to be used to run the Interface Listener job.
params, refer to the arguments that can be passed to the flow. For example, multiple parameters can be parsed as a key/value object from an external link or from a Const or JavaScript Actor.
Amazon S3 Storage Interface
The Amazon S3 Storage interface type is used to define the connections between S3 bucket and a data stream.
When creating an Interface Listener for a Broadway flow, an Amazon S3 Storage interface is required to detect new files added to S3.
Authentication
The AWS S3 interface supports two modes of authentication: 1) use of an Access Key and Secret Access Key, and 2) short-lived credentials using AWS STS and IRSA.
To learn how Fabric leverages AWS STS and IRSA, please refer to the How Fabric Leverages AWS IAM in a Kubernetes Environment article.
Creating the Interface
To create a new Amazon S3 Storage interface, do the following:
Go to Project Tree > Shared Objects, right click Interfaces, select New Interface and then select Amazon S3 Storage from the File System section to open the New Interface window.

Populate the connection's settings and click Save.
Go to Project Tree > Shared Objects, right click Interfaces, select New Interface and then select Amazon S3 Storage from the Interface Type dropdown menu to open the New Interface window.
Enter a suitable name for your new Amazon S3 Storage Interface, then click Create

Populate the connection's settings and click Save.

If the interface is supposed to be used for File Cataloging, expand the Discovery section and populate the names of 3 Broadway flows. This option is available starting from Fabric V8.3. Click here for more information about the File Cataloging solution.
Connection Settings
Click for more information about the File Cataloging solution.
Example of Using an Amazon S3 Storage Interface
To create an Interface Listener that runs on an S3 interface, do the following:
Create an interface using an Amazon S3 Storage interface type.
Create a Broadway flow either under Shared Objects or under the same Logical Unit. The flow reads data from a file using the predefined interface and populates it into the DB.

- Note that the interface and the path input arguments of the FileRead Actor are defined as External link type. Their values are passed from the defined interface by the Listener.
Add an InterfaceListener Actor to the "deploy.flow" flow, located at the Broadway folder. Use the Broadway flow, which you created in the previous step, as the
flowNameproperty in this actor.Deploy the LU to activate the Listener.
Using the InterfaceListener Actor
The InterfaceListener Actor enables the flow in which it is instantiated to listen to Amazon S3 Storage interface and trigger another Broadway flow upon arrival of a new file on the interface.
To create an Interface Listener job from a Broadway flow, add the InterfaceListener Actor to the flow.
Fill in the following parameters in the Actor's Properties tab:
flowName, the flow to be triggered by the Interface Listener.
interfaceName, the interface that is being listened and used to trigger the flow defined above, once a new file is detected on the file system to which the interface points.
affinity, sets which node/DC name IP address is to be used to run the Interface Listener job.
params, refer to the arguments that can be passed to the flow. For example, multiple parameters can be parsed as a key/value object from an external link or from a Const or JavaScript Actor.