TDM Generate Task
A Generate task generates synthetic entities. The synthetic entities can either be generated and saved in Fabric in order to be loaded later into the testing environment, or be generated and loaded into the target environment in one single task if the Load task action is checked with the Generate task action.
A Generate task can also include Load or Load + Reserve task actions and it contains the following tabs:
When checking the Set Task Variables setting, a new Task Variables tab opens.
Additional Execution Parameters Tab
The following execution parameters are set on Generate tasks:
Data Type
The data type supported for Generate task is Entities.
Reservation Settings
The Reservation Period and Reservation Note are displayed if the Reserve task action is checked in the task.
Retention Period
This is the retention period set for the generated entities. When this period ends, the entities are automatically deleted from Fabric and are no longer available.
Retention Period Values
Do not Delete - do not delete from Fabric. This is the default value.
Do not Retain - avoid saving the entities in Fabric (instead of saving and deleting). This option can be used, for example, to generate and load synthetic entities without saving the entities into Fabric.
Set unit of measure (Minutes, Hours, Days …) and value. For example, save the data in Fabric for 2 days. After 2 days the data are automatically deleted from Fabric.
Note that the retention period can be set in minutes, hours, days, weeks or years, depending on the maximum retention period set in the TDM DB. Both parameters - default retention period and maximum retention period - are set in the TDM DB.
Additional Execution Parameters
Set Task Variables
Check to open the Task Variables tab and set the variable value on a task level.
Post Execution Processes
Select all, partial, or one post execution process of the selected BE.
Requested Entities Tab
This tab defines the number of generated entities. The user can also set data generation parameters. For example, generate customers that live in Chicago.
TDM 8.0 added an integration of Broadway editors into the TDM portal when populating either the data generation parameters in the Requested Entities task’s tab.
This integration enables the user to select a valid value from a list, to set dates and to set distributed parameters:
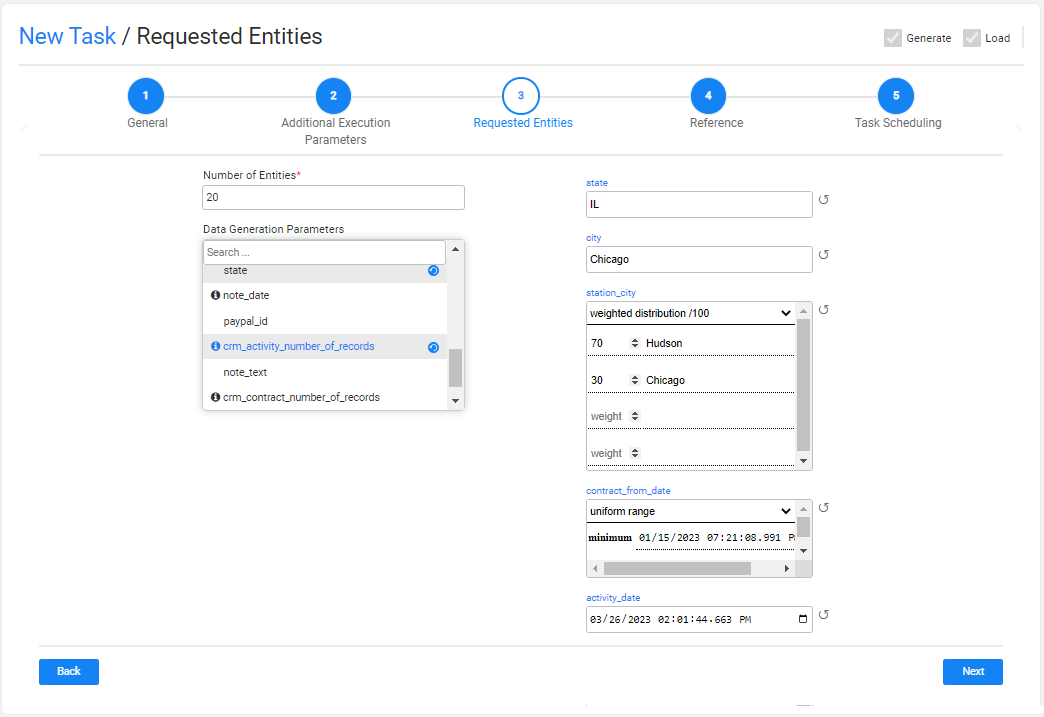
Note that the number of entities populated by the tester user is limited by their environment's permission set. This is the maximum number of entities of the task.
Adding Data Generation Parameters to the Task
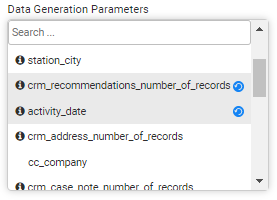
Select a parameter from the data generation parameter's list. You can add a search value to get the required parameter. The selected parameter is added to the window with the default values, if set.
The selected parameters are marked in grey and they get a blue Refresh icon next to the selected parameter's name:
Removing Data Generation Parameters from the Task
Click the blue Refresh icon next to the parameter's name in the data generation parameters list. The removed parameter returns back to its default value if set.
Reset the Data Generation Parameter's Value
Click the black Refresh icon next to the parameter's editor to reset your updates and get back to the previous value, if set. The previous value can be the default value or the previous value set by the user when opening and updating a Generate task.
Data Generation - Distribution Parameters
The distribution parameter generates random values according to input distribution settings. The supported distribution types are normal, uniform, weighted and constant (return one value).
The user can edit the distribution type and the related distribution parameters. The distribution parameters are set based on the selected distribution type:
Normal distribution (gaussian) works using mean and stddev (standard deviation), and can be bound by minimum and maximum values, both inclusive.
Example:
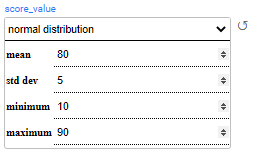
In the above example, the generated customers will get a score between 10-90. Most of the generated customers will get a score around 80 with a standard deviation of 5.
Uniform distribution returns a random value between the minimum and maximum values.
Example:
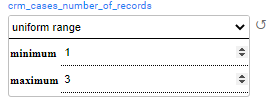
In the above example, the generated customers will have 1-3 cases for each generated activity.
Weighted distribution returns a value from the list, based on the value's weight. Weighted distribution uses a 'weights' map, where the keys are the results and the values are positive numbers indicating the weight of the entry of the whole. Both, the distributed values and the weights, need to be populated manually.
Example:
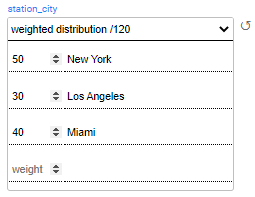
In the above example, 42% (50/120) of the generated customers will be attached to a station in New York, 25% (30/120) will be attached to a station in Los Angeles and 33% (40/120) will be attached to a station in Miami.
costant distribution returns the populated value. For example: set the number of generated addresses to 1 address per customer.
Example:
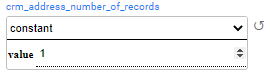
In the above example, the generated customers have only one address.
TDM Generate Task
A Generate task generates synthetic entities. The synthetic entities can either be generated and saved in Fabric in order to be loaded later into the testing environment, or be generated and loaded into the target environment in one single task if the Load task action is checked with the Generate task action.
A Generate task can also include Load or Load + Reserve task actions and it contains the following tabs:
When checking the Set Task Variables setting, a new Task Variables tab opens.
Additional Execution Parameters Tab
The following execution parameters are set on Generate tasks:
Data Type
The data type supported for Generate task is Entities.
Reservation Settings
The Reservation Period and Reservation Note are displayed if the Reserve task action is checked in the task.
Retention Period
This is the retention period set for the generated entities. When this period ends, the entities are automatically deleted from Fabric and are no longer available.
Retention Period Values
Do not Delete - do not delete from Fabric. This is the default value.
Do not Retain - avoid saving the entities in Fabric (instead of saving and deleting). This option can be used, for example, to generate and load synthetic entities without saving the entities into Fabric.
Set unit of measure (Minutes, Hours, Days …) and value. For example, save the data in Fabric for 2 days. After 2 days the data are automatically deleted from Fabric.
Note that the retention period can be set in minutes, hours, days, weeks or years, depending on the maximum retention period set in the TDM DB. Both parameters - default retention period and maximum retention period - are set in the TDM DB.
Additional Execution Parameters
Set Task Variables
Check to open the Task Variables tab and set the variable value on a task level.
Post Execution Processes
Select all, partial, or one post execution process of the selected BE.
Requested Entities Tab
This tab defines the number of generated entities. The user can also set data generation parameters. For example, generate customers that live in Chicago.
TDM 8.0 added an integration of Broadway editors into the TDM portal when populating either the data generation parameters in the Requested Entities task’s tab.
This integration enables the user to select a valid value from a list, to set dates and to set distributed parameters:

Note that the number of entities populated by the tester user is limited by their environment's permission set. This is the maximum number of entities of the task.
Adding Data Generation Parameters to the Task
Select a parameter from the data generation parameter's list. You can add a search value to get the required parameter. The selected parameter is added to the window with the default values, if set.
The selected parameters are marked in grey and they get a blue Refresh icon next to the selected parameter's name:

Removing Data Generation Parameters from the Task
Click the blue Refresh icon next to the parameter's name in the data generation parameters list. The removed parameter returns back to its default value if set.
Reset the Data Generation Parameter's Value
Click the black Refresh icon next to the parameter's editor to reset your updates and get back to the previous value, if set. The previous value can be the default value or the previous value set by the user when opening and updating a Generate task.
Data Generation - Distribution Parameters
The distribution parameter generates random values according to input distribution settings. The supported distribution types are normal, uniform, weighted and constant (return one value).
The user can edit the distribution type and the related distribution parameters. The distribution parameters are set based on the selected distribution type:
Normal distribution (gaussian) works using mean and stddev (standard deviation), and can be bound by minimum and maximum values, both inclusive.
Example:

In the above example, the generated customers will get a score between 10-90. Most of the generated customers will get a score around 80 with a standard deviation of 5.
Uniform distribution returns a random value between the minimum and maximum values.
Example:

In the above example, the generated customers will have 1-3 cases for each generated activity.
Weighted distribution returns a value from the list, based on the value's weight. Weighted distribution uses a 'weights' map, where the keys are the results and the values are positive numbers indicating the weight of the entry of the whole. Both, the distributed values and the weights, need to be populated manually.
Example:

In the above example, 42% (50/120) of the generated customers will be attached to a station in New York, 25% (30/120) will be attached to a station in Los Angeles and 33% (40/120) will be attached to a station in Miami.
costant distribution returns the populated value. For example: set the number of generated addresses to 1 address per customer.
Example:

In the above example, the generated customers have only one address.




