Globals Overview
What Are Globals?
Globals are predefined variables that can be accessed by different objects within a project and are used when the same information is required repeatedly by various Fabric objects. For example, to define the source application version or a date format in order use the same value in several Fabric objects.
- Globals are saved in a Java file as static variables and can be used by all Fabric object types like Project functions or Table Population objects.
- Globals can be defined as Final whereby they cannot be overridden in Java code or by a command that runs on the Fabric server.
- Globals that are not defined as Final can be overridden.
Click for more information about Global's override using SET and SET_GLOBAL commands.
The scope of a Global depends on how it is defined, which can be either:
- Shared Objects, whereby the Global is available to all objects in a project under all Logical Units, Reference Tables and Web Services.
- Logical Unit, whereby the Global is available within the specific Logical Unit where it is defined.
If the same Global is defined at both Shared Objects and Logical Unit levels, the Logical Unit definition is used within the scope of that Logical Unit. Other Logical Units use the Shared Objects definition.
The global variables are maintained in the SharedGlobals.java file located under Java/src in the Shared Objects or in the Globals.java file located under Java/src in the Logical Unit.
How Do I Create or Edit a Global?
- Do either:
- Go to Project Tree > Logical Units > [LU name] > Java and then click Globals.java to open the Globals window.
- Go to Project Tree > Shared Objects > Java and then click SharedGlobals.java to open the Globals window.
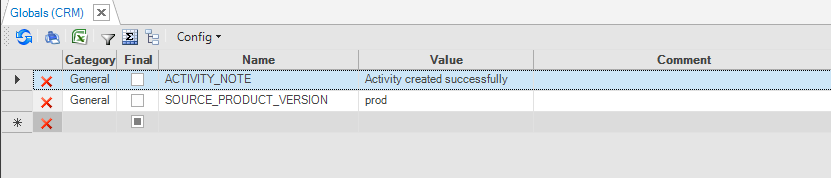
- Populate the settings as follows:
- Enter a Global Name in the Name column.
- Enter a value in the Value column.
- (Optional) Enter a Category in the Category column.
- (Optional) Enter a Comment in the Comment column.
- Check if the Global is Final.
- Click Save.
Notes
- Each Global defined via the Globals window is created in either Globals.java under the LU or in SharedGlobals.java under the Shared Object.
- A Global can be edited via the respective Globals window or by opening the source file in Fabric Studio.
- Go to Project Tree > Implementation > Logical Units/Data Products > [LU name] .
- Expand Java .
- A hierarchy tree will open. Drill down until you see Globals.java, and double click on it.
- Edit the Java file to add and define the global variable.
- Save the file (File -> Save or CTRL-S).
Click for more information about using Globals - Code Examples.
Globals Overview
What Are Globals?
Globals are predefined variables that can be accessed by different objects within a project and are used when the same information is required repeatedly by various Fabric objects. For example, to define the source application version or a date format in order use the same value in several Fabric objects.
- Globals are saved in a Java file as static variables and can be used by all Fabric object types like Project functions or Table Population objects.
- Globals can be defined as Final whereby they cannot be overridden in Java code or by a command that runs on the Fabric server.
- Globals that are not defined as Final can be overridden.
Click for more information about Global's override using SET and SET_GLOBAL commands.
The scope of a Global depends on how it is defined, which can be either:
- Shared Objects, whereby the Global is available to all objects in a project under all Logical Units, Reference Tables and Web Services.
- Logical Unit, whereby the Global is available within the specific Logical Unit where it is defined.
If the same Global is defined at both Shared Objects and Logical Unit levels, the Logical Unit definition is used within the scope of that Logical Unit. Other Logical Units use the Shared Objects definition.
The global variables are maintained in the SharedGlobals.java file located under Java/src in the Shared Objects or in the Globals.java file located under Java/src in the Logical Unit.
How Do I Create or Edit a Global?
- Do either:
- Go to Project Tree > Logical Units > [LU name] > Java and then click Globals.java to open the Globals window.
- Go to Project Tree > Shared Objects > Java and then click SharedGlobals.java to open the Globals window.

- Populate the settings as follows:
- Enter a Global Name in the Name column.
- Enter a value in the Value column.
- (Optional) Enter a Category in the Category column.
- (Optional) Enter a Comment in the Comment column.
- Check if the Global is Final.
- Click Save.
Notes
- Each Global defined via the Globals window is created in either Globals.java under the LU or in SharedGlobals.java under the Shared Object.
- A Global can be edited via the respective Globals window or by opening the source file in Fabric Studio.
- Go to Project Tree > Implementation > Logical Units/Data Products > [LU name] .
- Expand Java .
- A hierarchy tree will open. Drill down until you see Globals.java, and double click on it.
- Edit the Java file to add and define the global variable.
- Save the file (File -> Save or CTRL-S).
Click for more information about using Globals - Code Examples.



