Graphit Node Types
Node Types define how content is structured and how tags are presented in output documents. By default, nodes are assigned neither a Type nor a Property when they are created.
The following table lists and describes the available node types. Please refer to the Graphit file names that appear in the Examples column of the following table. These files can be found in the KB Demo Project under Project Tree > Web Services. We suggest that you run each Graphit file in a Debug mode and observe the response.
|
Node Type |
Description |
Examples |
| Field | Basic node type. Defines the node as a tag in XML/JSON format. | grField |
| Function | Runs the code to determine the value of the node. Note that the code must be written in JavaScript. | grFunction |
| SQL and SQL Non-prepared | Defines an SQL statement that retrieves information from Fabric or other database interfaces.
Enter the SQL statement manually or hover over and then click the DB icon to open the Query Builder.
Note: If the database is not Fabric, the Interface Name must be defined as described in the Node Properties section.
Note that it is recommended to set the SQL statement type to SQL to use a prepared statement and prepared binding. To build an SQL statement for each call, set the query type to SQL non-prepared. For example, to build dynamic SQL, select X,Y from $table name. |
grSQL |
| String | Simple string text or some combination with variables, such as input parameters or previous field nodes. | grString |
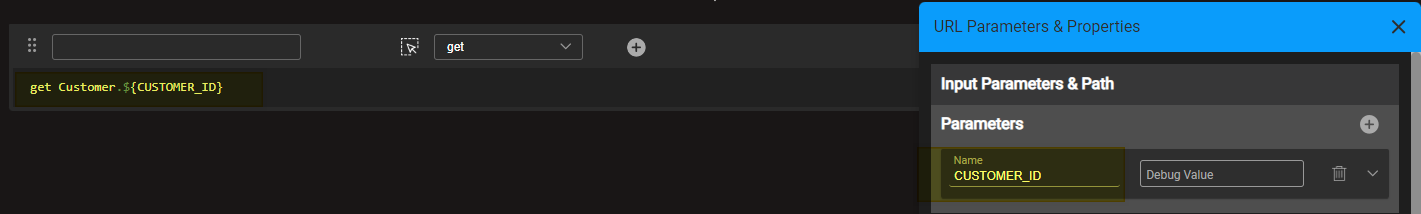
| Get | Defines the Fabric Get command, according to the LU and LU iid, which will be executed when invoking this Graphit file. Enter the Get command statement manually or hover over and then click the Helper icon (  ) to open the Command Builder. See more information later in this article. ) to open the Command Builder. See more information later in this article.
|
|
| Broadway | Defines a call to a Broadway flow that will be activated. Enter the command statement manually or hover over and then click the Helper icon (  ) to open the Command Builder. See more information later in this article. ) to open the Command Builder. See more information later in this article.
|
|
| Condition | Generates IF-ELSE statements that should include a condition. The nested nodes are/aren't executed according to the condition's result. | grCondition |
| Group | Groups several elements. It is used mainly with Condition nodes. | grGroup |
| Collect | Iterates multiple data sets into one unified array. | grCollect |
| Raw | Presents data as output without manipulation. For example, a header for an XML format. | grRaw |
| Include | Enables the inclusion of another Graphit file, where its output is embedded as part of the parent.
| grInclude |
Command Builders
Graphit Editor provides three builders — SQL Query Builder, Get Command Builder and Broadway Command Builder — in order to simplify the creation of Graphit file content. The SQL Query Builder opens the Studio's Query Builder.
SQL Query Builder
Upon selecting either 'sql' or ‘sql non-prepared’ as the node type and then clicking on the DB icon (a.k.a Query Builder) aside this field, the Query Builder pop-up window opens. This is where you are allowed to build SQL queries on a selected Interface (an external data source) as well as on Fabric.
Get Command Builder
Upon selecting 'get' as the node type or when clicking on the  icon of a node that is already populated with the 'get' node type, the Get Command Builder pop-up window opens.
icon of a node that is already populated with the 'get' node type, the Get Command Builder pop-up window opens.
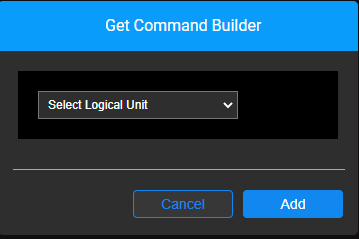
Select a Logical Unit and click 'Add'.
The pop-up window will close and the get command will appear with the appropriate syntax.
The iid parameter is smartly acquired from the Logical Unit root table iid, and populated; it is also automatically added as the Graphit file input parameter.
Broadway Command Builder
You can call and activate a Broadway flow from Graphit, and include it as part of the logic and output of the Graphit file.
Upon selecting 'broadway' as the node type or when clicking on the  icon of a node that is already populated with the 'broadway' node type, the Broadway Command Builder pop-up window opens.
icon of a node that is already populated with the 'broadway' node type, the Broadway Command Builder pop-up window opens.
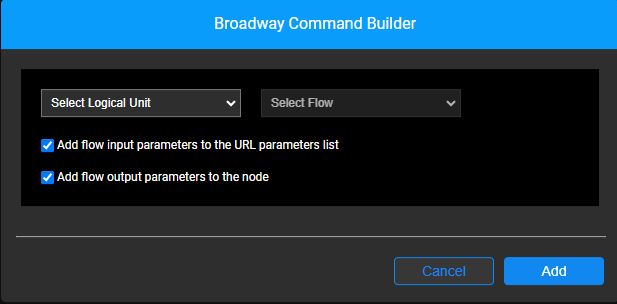
Select the Logical Unit in which the required Broadway flow is located.
Select the Broadway flow.
Choose whether the Broadway flow input parameters should be automatically added as input parameters in the Graphit file. This default option helps save time and reduce the risk of errors. However, you can uncheck this checkbox in cases where flow input parameters are manually pre-set in the Graphit file — either as constants or based on the results of a previous query.
Note: For simplicity, this checkbox affects all Broadway flow input parameters.
- Choose whether to add and present the Broadway flow output as fields in Graphit, or not. This option is similar to the one described in the SQL entry of the above table, where the Query Builder pop-up window closes and you are asked whether to present the SQL fields.
Graphit Node Types
Node Types define how content is structured and how tags are presented in output documents. By default, nodes are assigned neither a Type nor a Property when they are created.
The following table lists and describes the available node types. Please refer to the Graphit file names that appear in the Examples column of the following table. These files can be found in the KB Demo Project under Project Tree > Web Services. We suggest that you run each Graphit file in a Debug mode and observe the response.
|
Node Type |
Description |
Examples |
| Field | Basic node type. Defines the node as a tag in XML/JSON format. | grField |
| Function | Runs the code to determine the value of the node. Note that the code must be written in JavaScript. | grFunction |
| SQL and SQL Non-prepared | Defines an SQL statement that retrieves information from Fabric or other database interfaces.
Enter the SQL statement manually or hover over and then click the DB icon to open the Query Builder.
Note: If the database is not Fabric, the Interface Name must be defined as described in the Node Properties section.
Note that it is recommended to set the SQL statement type to SQL to use a prepared statement and prepared binding. To build an SQL statement for each call, set the query type to SQL non-prepared. For example, to build dynamic SQL, select X,Y from $table name. |
grSQL |
| String | Simple string text or some combination with variables, such as input parameters or previous field nodes. | grString |
| Get | Defines the Fabric Get command, according to the LU and LU iid, which will be executed when invoking this Graphit file. Enter the Get command statement manually or hover over and then click the Helper icon (  ) to open the Command Builder. See more information later in this article. ) to open the Command Builder. See more information later in this article.
|
|
| Broadway | Defines a call to a Broadway flow that will be activated. Enter the command statement manually or hover over and then click the Helper icon (  ) to open the Command Builder. See more information later in this article. ) to open the Command Builder. See more information later in this article.
|
|
| Condition | Generates IF-ELSE statements that should include a condition. The nested nodes are/aren't executed according to the condition's result. | grCondition |
| Group | Groups several elements. It is used mainly with Condition nodes. | grGroup |
| Collect | Iterates multiple data sets into one unified array. | grCollect |
| Raw | Presents data as output without manipulation. For example, a header for an XML format. | grRaw |
| Include | Enables the inclusion of another Graphit file, where its output is embedded as part of the parent.
| grInclude |
Command Builders
Graphit Editor provides three builders — SQL Query Builder, Get Command Builder and Broadway Command Builder — in order to simplify the creation of Graphit file content. The SQL Query Builder opens the Studio's Query Builder.
SQL Query Builder
Upon selecting either 'sql' or ‘sql non-prepared’ as the node type and then clicking on the DB icon (a.k.a Query Builder) aside this field, the Query Builder pop-up window opens. This is where you are allowed to build SQL queries on a selected Interface (an external data source) as well as on Fabric.
Get Command Builder
Upon selecting 'get' as the node type or when clicking on the  icon of a node that is already populated with the 'get' node type, the Get Command Builder pop-up window opens.
icon of a node that is already populated with the 'get' node type, the Get Command Builder pop-up window opens.

Select a Logical Unit and click 'Add'.
The pop-up window will close and the get command will appear with the appropriate syntax.
The iid parameter is smartly acquired from the Logical Unit root table iid, and populated; it is also automatically added as the Graphit file input parameter.

Broadway Command Builder
You can call and activate a Broadway flow from Graphit, and include it as part of the logic and output of the Graphit file.
Upon selecting 'broadway' as the node type or when clicking on the  icon of a node that is already populated with the 'broadway' node type, the Broadway Command Builder pop-up window opens.
icon of a node that is already populated with the 'broadway' node type, the Broadway Command Builder pop-up window opens.

Select the Logical Unit in which the required Broadway flow is located.
Select the Broadway flow.
Choose whether the Broadway flow input parameters should be automatically added as input parameters in the Graphit file. This default option helps save time and reduce the risk of errors. However, you can uncheck this checkbox in cases where flow input parameters are manually pre-set in the Graphit file — either as constants or based on the results of a previous query.
Note: For simplicity, this checkbox affects all Broadway flow input parameters.
- Choose whether to add and present the Broadway flow output as fields in Graphit, or not. This option is similar to the one described in the SQL entry of the above table, where the Query Builder pop-up window closes and you are asked whether to present the SQL fields.